Deciphering the Anticancer Arsenal of Piper longum: Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking Unveil Phytochemical Targets Against Lung Cancer
- PMID: 39113883
- PMCID: PMC11302554
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.98393
Deciphering the Anticancer Arsenal of Piper longum: Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking Unveil Phytochemical Targets Against Lung Cancer
Abstract
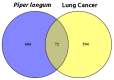
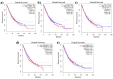
Introduction: Lung cancer, characterized by uncontrolled cellular proliferation within the lung tissues, is the predominant cause of cancer-related fatalities worldwide. The traditional medicinal herb Piper longum has emerged as a significant contender in oncological research because of its documented anticancer attributes, suggesting its potential for novel therapeutic development. Methods: This study adopted network pharmacology and omics methodology to elucidate the anti-lung cancer potential of P. longum by identifying its bioactive constituents and their corresponding molecular targets. Results: Through a comprehensive literature review and the Integrated Medicinal Plant Phytochemistry and Therapeutics database (IMPPAT), we identified 33 bioactive molecules from P. longum. Subsequent analyses employing tools such as SwissTargetPrediction, SuperPred, and DIGEP-Pred facilitated the isolation of 676 potential targets, among which 72 intersected with 666 lung cancer-associated genetic markers identified through databases including the Therapeutic Target Database (TTD), Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), and GeneCards. Further validation through protein-protein interaction (PPI) networks, gene ontology, pathway analyses, boxplots, and overall survival metrics underscored the therapeutic potential of compounds such as 7-epi-eudesm-4(15)-ene-1β, demethoxypiplartine, methyl 3,4,5-trimethoxycinnamate, 6-alpha-diol, and aristolodione. Notably, our findings reaffirm the relevance of lung cancer genes, such as CTNNB1, STAT3, HIF1A, HSP90AA1, and ERBB2, integral to various cellular processes and pivotal in cancer genesis and advancement. Molecular docking assessments revealed pronounced affinity between 6-alpha-diol and HIF1A, underscoring their potential as therapeutic agents for lung cancer. Conclusion: This study not only highlights the bioactive compounds of P. longum but also reinforces the molecular underpinnings of its anticancer mechanism, paving the way for future lung cancer therapeutics.
Keywords: Bioactivity; Computational screening; Drug discovery; Medicinal plant compounds; Oncogenes.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

