ICOS-ICOSL pathway enhances NKT-like cell antiviral function in pregnant women with COVID-19
- PMID: 39113896
- PMCID: PMC11302565
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.95952
ICOS-ICOSL pathway enhances NKT-like cell antiviral function in pregnant women with COVID-19
Abstract
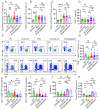
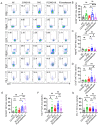
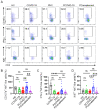
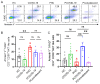
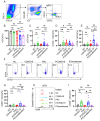
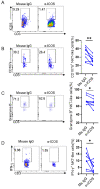
Objective: The immune response initiated by SARS-CoV-2 infection in pregnancy is poorly elucidated. We aimed to access and compare the antiviral cellular responses and lymphocytes activation between healthy pregnancies and pregnant women infected with SARS-CoV-2. Methods: We detected the immunological changes of lymphocytes in peripheral blood of healthy non-pregnant women, non-pregnant women with COVID-19, healthy pregnant women, pregnant women with COVID-19 and convalescent group by flow cytometry. In vitro blockade was used to identify NKT-like cell activation through ICOS-ICOSL pathway. Results: We found that CD3+CD56+ NKT-like cells decreased significantly in COVID-19 positive pregnant women compared to healthy pregnant women. NKT-like cells of pregnant women expressed higher level of activating receptors CD69 and NKp46 after SARS-CoV-2 infection. Particularly, they also increased the expression of the co-stimulatory molecule ICOS. NKT-like cells of pregnant women with COVID-19 up-regulated the expression of IFN-γ, CD107a and Ki67. Meanwhile, we found that ICOSL expression was significantly increased on pDCs in pregnant women with COVID-19. Blocking ICOS in vitro significantly decreased the antiviral activity of NKT-like cells in COVID-19 positive pregnant women, suggesting that ICOS-ICOSL may play an important role in the virus clearance by NKT-like cells. Conclusions: During SARS-CoV-2 infection, NKT-like cells of pregnant women activated through ICOS-ICOSL pathway and played an important role in the antiviral response.
Keywords: CD3+CD56+ NKT-like cells; COVID-19; ICOS; Pregnancy.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ICOS/ICOSL upregulation mediates inflammatory response and endothelial dysfunction in type 2 diabetes mellitus.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018 Dec;22(24):8898-8908. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201812_16659. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30575933
-
Inducible T-Cell Costimulator Mediates Lymphocyte/Macrophage Interactions During Liver Repair.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 3;12:786680. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.786680. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34925367 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the Long-Term Impact on Cellular Immunity in COVID-19-Recovered Individuals Reveals a Profound NKT Cell Impairment.mBio. 2021 Apr 27;12(2):e00085-21. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00085-21. mBio. 2021. PMID: 33906918 Free PMC article.
-
The rationale behind targeting the ICOS-ICOS ligand costimulatory pathway in cancer immunotherapy.ESMO Open. 2020 Jan;5(1):e000544. doi: 10.1136/esmoopen-2019-000544. ESMO Open. 2020. PMID: 32516116 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural killer cells and unconventional T cells in COVID-19.Curr Opin Virol. 2021 Aug;49:176-182. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2021.06.005. Epub 2021 Jun 19. Curr Opin Virol. 2021. PMID: 34217135 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Single-cell RNA-sequencing highlights a curtailed NK cell function in convalescent COVID-19 pregnant women.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 30;16:1560391. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1560391. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40661959 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li S, Li XB, Liang HW, Yu KK, Zhai JB, Xue MZ. et al. SARS-CoV-2 ORF7a blocked autophagy flux by intervening in the fusion between autophagosome and lysosome to promote viral infection and pathogenesis. Journal of Medical Virology. 2023;95:e29200. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

