Amphiphilic Janus Particles for Aerobic Alcohol Oxidation in Oil Foams
- PMID: 39114089
- PMCID: PMC11301628
- DOI: 10.1021/acscatal.4c00909
Amphiphilic Janus Particles for Aerobic Alcohol Oxidation in Oil Foams
Abstract
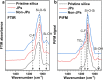
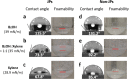
Amphiphilic Janus silica particles, tunable with oleophobic-oleophilic properties and low fluorine content (8 wt % F), exhibited prominent foamability for a variety of aromatic alcohols at low particle concentrations (<1 wt %) compared to randomly functionalized silica particles. When selectively loaded with Pd nanoparticles on the oleophilic hemisphere, the particles displayed more than a 2-fold increase in catalytic activity for the aerobic oxidation of benzyl alcohol compared to nonfoam bulk catalysis under ambient O2 pressure. The particles were conveniently recycled with high foamability and catalytic activity maintained for at least five consecutive runs.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures





References
-
- Yekeen N.; Manan M. A.; Idris A. K.; Padmanabhan E.; Junin R.; Samin A. M.; Gbadamosi A. O.; Oguamah I. A Comprehensive Review of Experimental Studies of Nanoparticles-Stabilized Foam for Enhanced Oil Recovery. J. Petroleum Sci. Eng. 2018, 164, 43–74. 10.1016/j.petrol.2018.01.035. - DOI
-
- Deotale S.; Dutta S.; Moses J.; Balasubramaniam V.; Anandharamakrishnan C. Foaming Characteristics of Beverages and its Relevance to Food Processing. Food Eng. Rev. 2020, 12, 229–250. 10.1007/s12393-020-09213-4. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
