The Prevalence of Rickettsial and Rickettsial-Like Diseases in Patients with Undifferentiated Febrile Illness - Hainan Province, China, 2018-2021
- PMID: 39114313
- PMCID: PMC11301603
- DOI: 10.46234/ccdcw2024.165
The Prevalence of Rickettsial and Rickettsial-Like Diseases in Patients with Undifferentiated Febrile Illness - Hainan Province, China, 2018-2021
Abstract
Introduction: Rickettsial and Rickettsial-like diseases, resulting from obligate intracellular Gram-negative bacteria, pose a growing public health threat in China. To assess the current prevalence of these diseases on Hainan Island, a study was conducted on 9 bacterial pathogens found in patients with undifferentiated febrile illness (UFI) treated in Haikou between 2018 and 2021 using a TaqMan Polymerase Chain Reaction (TaqMan PCR) array.
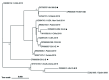
Methods: Blood samples (n=503) were collected from patients with UFI between 2018 and 2021. The samples were screened for Rickettsia spp., Orientia tsutsugamushi (O. tsutsugamushi), Anaplasma. phagocytophilum (A. phagocytophilum), Ehrlichia chaffeensis, Coxiella burnetii, Chlamydia psittaci, Brucella spp., Burkholderia pseudomallei, and Borrelia burgdorferi using a TaqMan PCR array. Positive samples (Ct<35) underwent confirmation through nested PCR, sequencing, and phylogenetic analysis.
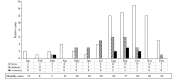
Results: O. tsutsugamushi and A. phagocytophilum were detected in the patients at positive rates of 14.51% (73/503) and 5.57% (28/503), respectively. Co-infection of O. tsutsugamushi and A. phagocytophilum was identified in scrub typhus (ST) positive populations from Hainan (10.96%, 8/73), Guangxi (61.54%, 8/13), and Yunnan (5.36%, 3/56) provincial-level administrative divisions (PLADs) of China.
Conclusion: An increased prevalence rate of ST and a decreased prevalence of rickettsioses were observed in patients with UFI in Hainan compared to a decade ago. The co-infection of O. tsutsugamushi and A. phagocytophilum poses a current public health threat in China.
Keywords: Anaplasma phagocytophilum; Orientia tsutsugamushi; Rickettsia; coinfection.
Copyright and License information: Editorial Office of CCDCW, Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Molecular epidemic survey on co-prevalence of scrub typhus and marine typhus in Yuxi city, Yunnan province of China.Chin Med J (Engl). 2007 Aug 5;120(15):1314-8. Chin Med J (Engl). 2007. PMID: 17711736
-
Optimization and Evaluation of a Multiplex Quantitative PCR Assay for Detection of Nucleic Acids in Human Blood Samples from Patients with Spotted Fever Rickettsiosis, Typhus Rickettsiosis, Scrub Typhus, Monocytic Ehrlichiosis, and Granulocytic Anaplasmosis.J Clin Microbiol. 2020 Aug 24;58(9):e01802-19. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01802-19. Print 2020 Aug 24. J Clin Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32493778 Free PMC article.
-
Concurrent Infection of Orientia Tsutsugamushi with Rickettsia spp. Including Rickettsia felis in North Central Bangladesh.Mymensingh Med J. 2022 Apr;31(2):350-354. Mymensingh Med J. 2022. PMID: 35383749
-
Rickettsioses in Children - A Review.Indian J Pediatr. 2020 Nov;87(11):930-936. doi: 10.1007/s12098-020-03216-z. Epub 2020 Feb 28. Indian J Pediatr. 2020. PMID: 32112308 Review.
-
The Isolation of Orientia tsutsugamushi and Rickettsia typhi from Human Blood through Mammalian Cell Culture: a Descriptive Series of 3,227 Samples and Outcomes in the Lao People's Democratic Republic.J Clin Microbiol. 2020 Nov 18;58(12):e01553-20. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01553-20. Print 2020 Nov 18. J Clin Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32999008 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
-
Wu J, Wang SL, Ma Y, Zeng XJ, Jia PB, Nie SF. Analysis of the detection results of rickettsial disease among patients with fever in Hainan province from 2009 to 2011. Chin J Health Lab Technol 2015;25(9):1311-13,1316. https://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/periodical/ChlQZXJpb2RpY2FsQ0hJTmV3UzIwMjQwNzA0EhF6Z3dzanl6ejIwMTUwOTAwNBoIbmt6bjc4ZWM%3D. (In Chinese).
-
-
- Xie XF, Wang GY, Huang Y, Tang CN, Peng RY, Hu XY, et al A review of the epidemic and clinical study on scrub typhus in China (2010–2020) J Hainan Med Univ. 2023;(19):57–61. doi: 10.13210/j.cnki.jhmu.20220802.001. - DOI
-
- Zhang Y, Hai Y, Teng ZQ, Xie XF, Xiong YW, Shao ZJ, et al Investigation of 9 pathogenic intracellular bacteria in blood samples from outpatients with undefined febrile illness. Dis Surv. 2022;37(4):457–63. doi: 10.3784/jbjc.202201200010. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
