Causal Association Between Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Alzheimer's Disease: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study
- PMID: 39114544
- PMCID: PMC11305840
- DOI: 10.3233/ADR-240053
Causal Association Between Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Alzheimer's Disease: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study
Abstract
Background: There is now increasing evidence that type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is associated with Alzheimer's disease (AD). However, it is unclear whether the two are causally related.
Objective: To reveal the causal association between T2DM and AD, we performed a bidirectional Mendelian randomization (MR) analysis.
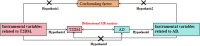
Methods: Genetic instrumental variables were systematically screened, and inverse-variance weighting, MR-Egger regression, weighted median, simple mode, and weighted mode were applied to assess the pathogenic associations between the two diseases, and sensitivity analyses were used to further validate the robustness of the results.
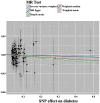
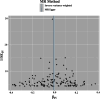
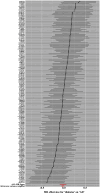
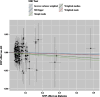
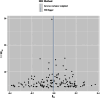
Results: The results of forward MR analysis with T2DM as the exposure were [OR = 0.998, 95% CI (0.975∼1.021), p = 0.857], and the results of reverse MR analysis with AD as the exposure were [OR = 0.966, 95% CI (0.934∼0.999), p = 0.043]. The results showed no significant association between T2DM and AD at the gene level (p < 0.025). Sensitivity analyses were consistent with the results of the main analysis, confirming the robustness of the study.
Conclusions: T2DM and AD may not be genetically causally associated.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Mendelian randomization; causal association; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
© 2024 – The authors. Published by IOS Press.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to report.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

