Optimizing UVA and UVC synergy for effective control of harmful cyanobacterial blooms
- PMID: 39114557
- PMCID: PMC11305005
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ese.2024.100455
Optimizing UVA and UVC synergy for effective control of harmful cyanobacterial blooms
Abstract
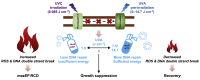
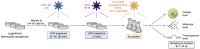
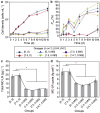
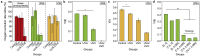
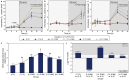
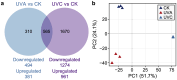
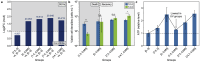
Harmful cyanobacterial blooms (HCBs) pose a global ecological threat. Ultraviolet C (UVC) irradiation at 254 nm is a promising method for controlling cyanobacterial proliferation, but the growth suppression is temporary. Resuscitation remains a challenge with UVC application, necessitating alternative strategies for lethal effects. Here, we show synergistic inhibition of Microcystis aeruginosa using ultraviolet A (UVA) pre-irradiation before UVC. We find that low-dosage UVA pre-irradiation (1.5 J cm-2) combined with UVC (0.085 J cm-2) reduces 85% more cell densities compared to UVC alone (0.085 J cm-2) and triggers mazEF-mediated regulated cell death (RCD), which led to cell lysis, while high-dosage UVA pre-irradiations (7.5 and 14.7 J cm-2) increase cell densities by 75-155%. Our oxygen evolution tests and transcriptomic analysis indicate that UVA pre-irradiation damages photosystem I (PSI) and, when combined with UVC-induced PSII damage, synergistically inhibits photosynthesis. However, higher UVA dosages activate the SOS response, facilitating the repair of UVC-induced DNA damage. This study highlights the impact of UVA pre-irradiation on UVC suppression of cyanobacteria and proposes a practical strategy for improved HCBs control.
Keywords: Cyanobacterial bloom; DNA damage/repair; Photosynthetic damage; Regulated cell death; Ultraviolet irradiation.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Dai R., Xiong Y., Ma Y., Tang T. Algae removal performance of UV-radiation-enhanced coagulation for two representative algal species. Sci. Total Environ. 2020;745 - PubMed
-
- Santos A.A., Guedes D.O., Barros M.U.G., Oliveira S., Pacheco A.B.F., Azevedo S.M.F.O., Magalhães V.F., Pestana C.J., Edwards C., Lawton L.A., Capelo-Neto J. Effect of hydrogen peroxide on natural phytoplankton and bacterioplankton in a drinking water reservoir: mesocosm-scale study. Water Res. 2021;197 - PubMed
-
- Zhu X., Dao G., Tao Y., Zhan X., Hu H. A review on control of harmful algal blooms by plant-derived allelochemicals. J. Hazard Mater. 2021;401 - PubMed
-
- Tao Y., Hou D., Zhou T., Cao H., Zhang W., Wang X. UV-C suppression on hazardous metabolites in Microcystis aeruginosa: unsynchronized production of microcystins and odorous compounds at population and single-cell level. J. Hazard Mater. 2018;359:281–289. - PubMed
-
- Žegura B., Štraser A., Filipič M. Genotoxicity and potential carcinogenicity of cyanobacterial toxins-A review. Rev. Mutat. Res. 2011;727:16–41. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

