Exercise motivation, physical exercise, and mental health among college students: examining the predictive power of five different types of exercise motivation
- PMID: 39114587
- PMCID: PMC11303313
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1356999
Exercise motivation, physical exercise, and mental health among college students: examining the predictive power of five different types of exercise motivation
Abstract
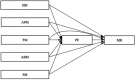
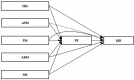
Introduction: The mental health (MH) of college students has long been a crucial concern for families, educational institutions, and society. Extensive research has demonstrated the influential role of exercise motivation in shaping MH. However, further investigation is warranted to ascertain which types of exercise motivation may have more influence on the MH of college students. The present study examined the direct effects of five distinct types of exercise motivation, namely health motivation (HM), appearance motivation (APM), fun motivation (FM), ability motivation (ABM), and social motivation (SM) on MH. Additionally, the study explored the potential mediating role of physical exercise (PE) in these relationships.
Methods: An cross-sectional study design was employed. A total of 433 Chinese college students participated in the study and completed our questionnaires, which included the Exercise motivation scale (EM scale), the Physical exercise scale (PE scale), and the Mental health scale (MH scale).
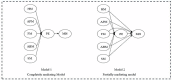
Results: The findings revealed a significant and positive relationship between all five categories of exercise motivation and the MH of college students. Specifically, FM was found to have the most pronounced impact on MH, followed by HM, ABM, SM, and APM, in descending order of influence. Furthermore, the impacts of HM, FM, ABM, and SM on MH were found to be partially mediated by PE. However, the association between APM and MH was entirely mediated by PE.
Discussion: The present study contributes to enhancing the comprehension of the underlying mechanisms behind different exercise motivations in relation to PE and MH. Additionally, it offers practical implications for developing intervention strategies for improving the MH of college students.
Keywords: college students; exercise motivation; mental health; physical exercise; predictive power.
Copyright © 2024 Li, Wang, Pan, Hu, Yin and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The influence of physical exercise on achievement motivation among college students: the mediating roles of self-efficacy and life satisfaction.Front Psychol. 2025 Jan 29;16:1529829. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1529829. eCollection 2025. Front Psychol. 2025. PMID: 39944037 Free PMC article.
-
The influence of physical exercise on college students' mental health and social adaptability from the cognitive perspective.Work. 2021;69(2):651-662. doi: 10.3233/WOR-213506. Work. 2021. PMID: 34120942
-
The impact of sports preferences on physical activity participation among college students: the mediating role of sports achievement emotions and exercise motivation.Front Psychol. 2025 Apr 28;16:1565998. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1565998. eCollection 2025. Front Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40357484 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of procrastination on physical activity among Chinese university students: the chain-mediated effects of time management disposition and exercise motivation.Front Psychol. 2024 Nov 15;15:1433880. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1433880. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 39618996 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise Effect on Mental Health in Isolating or Quarantining Adults.Aerosp Med Hum Perform. 2023 Sep 1;94(9):686-695. doi: 10.3357/AMHP.6073.2023. Aerosp Med Hum Perform. 2023. PMID: 37587629
Cited by
-
Analysis of the mechanism of physical activity enhancing well-being among college students using artificial neural network.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 16;15(1):25855. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-11269-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40670561 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the exercise intention-behavior gap among college students using explainable machine learning.Front Public Health. 2025 Jul 25;13:1613553. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1613553. eCollection 2025. Front Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40786156 Free PMC article.
-
The influence of physical exercise on achievement motivation among college students: the mediating roles of self-efficacy and life satisfaction.Front Psychol. 2025 Jan 29;16:1529829. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1529829. eCollection 2025. Front Psychol. 2025. PMID: 39944037 Free PMC article.
-
The negative aspects of injury on motivation of sports and physical exercise practitioners.Front Psychol. 2025 Feb 6;16:1520893. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1520893. eCollection 2025. Front Psychol. 2025. PMID: 39981398 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of physical exercise on adolescent social anxiety: the serial mediating effects of sports self-efficacy and expressive suppression.BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2025 Mar 22;17(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s13102-025-01107-4. BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2025. PMID: 40121514 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alimour S. A., Rish A., Abu M. A., Alqawasmi A. A. (2023). Exploring role of metacognitive components and their awareness in mental health behavior among students of higher educational institutions. Am. J. Health Behav. 47, 904–917. doi: 10.5993/AJHB.47.5.4 - DOI
-
- Allen D., Jay B. (2022). OPAL: Promoting mental health through friendship, socialisation and physical activity. Project Report, Manchester Metropolitan University. Available at: https://e-space.mmu.ac.uk/id/eprint/630413
-
- Bagozzi R. P., Yi Y. (1988). On the evaluation of structural equation models. J. Acad. Market Sci. 16, 74–94. doi: 10.1007/BF02723327 - DOI
-
- Benesty J., Chen J., Huang Y., Cohen I. (2009). Noise reduction in speech processing. New York: Springer.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

