Guselkumab Reduces Disease- and Mechanism-Related Biomarkers More Than Adalimumab in Patients with Psoriasis: A VOYAGE 1 Substudy
- PMID: 39114670
- PMCID: PMC11305298
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xjidi.2024.100287
Guselkumab Reduces Disease- and Mechanism-Related Biomarkers More Than Adalimumab in Patients with Psoriasis: A VOYAGE 1 Substudy
Abstract
Background: Psoriasis is an immune-mediated inflammatory disease characterized by activation of IL-23-driven IL-17-producing T cell and other IL-23 receptor-positive IL-17-producing cell responses. Selective blockade of IL-23p19 with guselkumab was superior to blockade of TNF-α with adalimumab (ADA) in treating moderate-to-severe psoriasis. Objective: Pharmacodynamic responses of guselkumab versus ADA were compared in patients with psoriasis in VOYAGE 1.
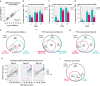
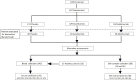
Design: Inflammatory cytokine serum levels were assessed (n = 118), and lesional and nonlesional skin biopsies were collected (n = 38) in patient subsets at baseline and 4, 24, and 48 weeks after treatment to evaluate pharmacodynamic responses of guselkumab versus those of ADA.
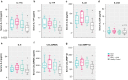
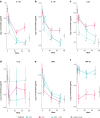
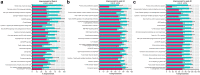
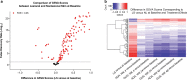
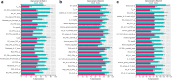
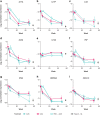
Results: Guselkumab provided rapid reductions in serum IL-17A, IL-17F, and IL-22 levels by week 4 versus at baseline, which were maintained through weeks 24 and 48 (P < .001). The magnitude of reduction of IL-17A and IL-22 at week 48 and IL-17F at weeks 4, 24, and 48 were greater with guselkumab than with ADA (all P < .05). In the skin, guselkumab reduced the expression of IL-23/IL-17 pathway-associated and psoriasis-associated genes.
Conclusion: These data provide extensive characterization of pharmacodynamic anti-inflammatory responses to IL-23p19 and TNF-α inhibition in human blood and tissue over time with FDA-approved doses of guselkumab and ADA. Trial registration:ClinicalTrials.govClinicalTrials.gov (NCT02207231).
Keywords: Adalimumab; Biomarkers; Guselkumab; IL-23/IL-17 pathway; Psoriasis.
© 2024 The Authors.
Figures
References
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

