Efficacy of exercise interventions combined with Selegiline in ameliorating freezing of gait in Parkinson's disease patients
- PMID: 39114711
- PMCID: PMC11301470
- DOI: 10.62347/JTRH2408
Efficacy of exercise interventions combined with Selegiline in ameliorating freezing of gait in Parkinson's disease patients
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the efficacy of exercise interventions combined with Selegiline in ameliorating freezing of gait (FOG) in Parkinson's disease (PD) patients.
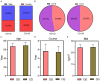
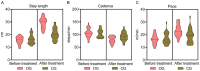
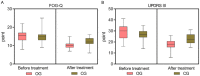
Methods: A total of 60 PD patients with FOG treated in the First People's Hospital of Fuyang District from January 2020 to January 2023 were retrospectively collected and analyzed. Patients were divided into a control group (n = 28, treated with Selegiline alone) and an observation group (n = 32, treated with Selegiline and exercise interventions). Gait parameters, FOG indices, motor and balance functions, Berg Balance, psychological status, and quality of life were compared between the groups pre- and post-treatment.
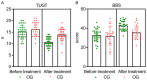
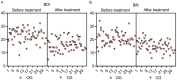
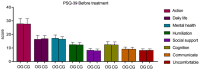
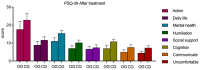
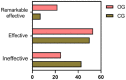
Results: After treatment, the observation group exhibited longer step length, higher step speed, and lower step frequency (P = 0.000, 0.003, 0.001, respectively), with enhanced balance as indicated by lower Timed Up and Go Test and higher Berg Balance Scale scores than the control group (P = 0.000, 0.000, respectively). The Beck Depression Inventory and Beck Anxiety Inventory scores were notably lower in the observation group than those in the control group (P = 0.000, 0.004, respectively). Additionally, the observation group showed better quality of life across several dimensions of the Parkinson's Disease Quality of Life Questionnaire, including mobility, activities of daily living, emotional well-being, stigma, social support, cognition, communication, and bodily discomfort (P = 0.000, 0.000, 0.000, 0.000, 0.017, 0.000, 0.000, 0.000, respectively) than the control group.
Conclusion: The combination of exercise interventions and Selegiline effectively rectifies the gait parameters, enhances the balance function, alleviates psychological distress, and improves the overall quality of life in PD patients experiencing FOG.
Keywords: Exercise intervention; Parkinson’s disease; Selegilin; balance function; freezing of gait.
AJTR Copyright © 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of music-based movement therapy on the freezing of gait in patients with Parkinson's disease: A randomized controlled trial.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Oct 19;14:924784. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.924784. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36337701 Free PMC article.
-
Postural sensory correlates of freezing of gait in Parkinson's disease.Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2016 Apr;25:72-7. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2016.02.004. Epub 2016 Feb 3. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2016. PMID: 26883663
-
Erratum.Mult Scler. 2016 Oct;22(12):NP9-NP11. doi: 10.1177/1352458515585718. Epub 2015 Jun 3. Mult Scler. 2016. PMID: 26041800
-
The effect of rehabilitation interventions on freezing of gait in people with Parkinson's disease is unclear: a systematic review and meta-analyses.Disabil Rehabil. 2023 Sep;45(19):3199-3218. doi: 10.1080/09638288.2022.2120099. Epub 2022 Sep 15. Disabil Rehabil. 2023. PMID: 36106644
-
Self-directed physical activity interventions for motor symptoms and quality of life in early and mid-stage Parkinson's disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2024 Jan;116:105159. doi: 10.1016/j.archger.2023.105159. Epub 2023 Aug 13. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2024. PMID: 37625216
References
-
- Capecci M, Pournajaf S, Galafate D, Sale P, Le Pera D, Goffredo M, De Pandis MF, Andrenelli E, Pennacchioni M, Ceravolo MG, Franceschini M. Clinical effects of robot-assisted gait training and treadmill training for Parkinson’s disease. A randomized controlled trial. Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 2019;62:303–312. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
