A Prospective, Single-Arm, Phase 2 Study of Modified Transarterial Chemoembolization Using Low-Dose Chemotherapy with Blank Microspheres Plus Low-Dose Lenvatinib and Microwave Ablation in Patients with Large (≥7 cm) Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma: The TALEM Trial
- PMID: 39114763
- PMCID: PMC11305670
- DOI: 10.1159/000536518
A Prospective, Single-Arm, Phase 2 Study of Modified Transarterial Chemoembolization Using Low-Dose Chemotherapy with Blank Microspheres Plus Low-Dose Lenvatinib and Microwave Ablation in Patients with Large (≥7 cm) Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma: The TALEM Trial
Abstract
Introduction: For patients with large unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the effectiveness of conventional transarterial chemoembolization (cTACE) remains suboptimal. This study investigated the efficacy and safety of modified TACE using low-dose chemotherapy with blank microspheres (BMS-TACE) plus low-dose lenvatinib (LD-LEN) and microwave ablation (MWA) in patients with large unresectable HCC.
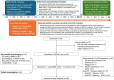
Methods: In this prospective, single-arm, phase 2 study, patients with unresectable HCC exceeding the up-to-seven criteria, with maximum tumor diameter ≥7 cm, and without macrovascular invasion or extrahepatic metastases, received initial BMS-TACE (lipiodol, low-dose doxorubicin, and lobaplatin up to 30 mg each, and blank microspheres; subsequently modified and repeated in most patients) plus LD-LEN (4-8 mg/day) and MWA. The primary endpoint was downstaging rate (DSR); secondary endpoints were objective response rate (ORR), progression-free survival (PFS), overall survival (OS), and adverse events.
Results: From November 2019 to March 2022, 43 patients were enrolled. Median follow-up was 21.2 months. Median largest tumor diameter was 11.2 cm (interquartile range [IQR], 7-25). Following BMS-TACE and LD-LEN, downstaging occurred in 37 (86.0%) patients, 32 of whom received MWA, and 8 of whom had a complete response (CR) without MWA. ORR was 93.0% (CR in 32 [74.4%] and partial response in 8 [18.6%] patients). The 1-, 2-, and 3-year PFS rates were 57.5%, 25.9%, and 18.1%, respectively (median PFS, 14.7 months [95% CI: 8.1-19.5]). The 1-, 2-, and 3-year OS rates were 85.8%, 67.7%, and 61.6%, respectively (median OS, 36.4 months [95% CI: 26.8-not reached]). After BMS-TACE, a significant decline in CD11b+/CD33+/HLA-DR- myeloid-derived suppressor cells and early elevation in CXCR5+/CD8+ and CXCR5+/CD4+ T cells were observed (both p < 0.05).
Conclusion: BMS-TACE plus LD-LEN and MWA resulted in promising efficacy and tolerable toxicity in patients with large unresectable HCC exceeding the up-to-seven criteria with a maximum tumor diameter ≥7 cm and without macrovascular invasion or extrahepatic metastases.
Keywords: Blank microsphere transarterial chemoembolization; Large unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma; Levatinib.
© 2024 The Author(s). Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209–49. - PubMed
-
- Lencioni R, de Baere T, Soulen MC, Rilling WS, Geschwind JF. Lipiodol transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review of efficacy and safety data. Hepatology. 2016;64(1):106–16. - PubMed
-
- Galle PR, Tovoli F, Foerster F, Worns MA, Cucchetti A, Bolondi L. The treatment of intermediate stage tumours beyond TACE: from surgery to systemic therapy. J Hepatol. 2017;67(1):173–83. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

