Management of older adults with diabetes mellitus: Perspective from geriatric medicine
- PMID: 39115890
- PMCID: PMC11442781
- DOI: 10.1111/jdi.14283
Management of older adults with diabetes mellitus: Perspective from geriatric medicine
Abstract
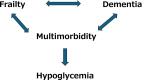
Advances in diabetes medication and population aging are lengthening the lifespans of people with diabetes mellitus (DM). Older patients with diabetes mellitus often have multimorbidity and tend to have polypharmacy. In addition, diabetes mellitus is associated with frailty, functional decline, cognitive impairment, and geriatric syndrome. Although the numbers of patients with frailty, dementia, disability, and/or multimorbidity are increasing worldwide, the accumulated evidence on the safe and effective treatment of these populations remains insufficient. Older patients, especially those older than 75 years old, are often underrepresented in randomized controlled trials of various treatment effects, resulting in limited clinical evidence for this population. Therefore, a deeper understanding of the characteristics of older patients is essential to tailor management strategies to their needs. The clinical guidelines of several academic societies have begun to recognize the importance of relaxing glycemic control targets to prevent severe hypoglycemia and to maintain quality of life. However, glycemic control levels are thus far based on expert consensus rather than on robust clinical evidence. There is an urgent need for the personalized management of older adults with diabetes mellitus that considers their multimorbidity and function and strives to maintain a high quality of life through safe and effective medical treatment. Older adults with diabetes mellitus accompanied by frailty, functional decline, cognitive impairment, and multimorbidity require special management considerations and liaison with both carers and social resources.
Keywords: Frailty; Multimorbidity; Polypharmacy.
© 2024 The Author(s). Journal of Diabetes Investigation published by Asian Association for the Study of Diabetes (AASD) and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Individualized treatment of diabetes mellitus in older adults.Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2024 Dec;24(12):1257-1268. doi: 10.1111/ggi.14979. Epub 2024 Oct 7. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2024. PMID: 39375857 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toward the development of a vibrant, super-aged society: The future of medicine and society in Japan.Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2021 Aug;21(8):601-613. doi: 10.1111/ggi.14201. Epub 2021 Jul 1. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2021. PMID: 34212470
-
Glycemic targets and medication limitations for type 2 diabetes mellitus in the older adult.Consult Pharm. 2014 Feb;29(2):110-23. doi: 10.4140/TCP.n.2014.110. Consult Pharm. 2014. PMID: 24513421 Review.
-
Management of Type 2 Diabetes in Frail Older Adults.Drugs Aging. 2023 Sep;40(9):751-761. doi: 10.1007/s40266-023-01049-x. Epub 2023 Jul 11. Drugs Aging. 2023. PMID: 37434085
-
New horizons in multimorbidity in older adults.Age Ageing. 2017 Nov 1;46(6):882-888. doi: 10.1093/ageing/afx150. Age Ageing. 2017. PMID: 28985248 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Diabetes in Korean Adults: Prevalence, Management, and Comorbidities.Diabetes Metab J. 2025 Jan;49(1):22-23. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2024.0844. Epub 2025 Jan 1. Diabetes Metab J. 2025. PMID: 39828975 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Challenges, current innovations, and opportunities for managing type 2 diabetes in frail older adults: a position paper of the European Geriatric Medicine Society (EuGMS)-Special Interest Group in Diabetes.Eur Geriatr Med. 2025 Feb 27. doi: 10.1007/s41999-025-01168-1. Online ahead of print. Eur Geriatr Med. 2025. PMID: 40014274 Review.
-
Frailty, multimorbidity, and polypharmacy: Proposal of the new concept of the geriatric triangle.Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2025 May;25(5):657-662. doi: 10.1111/ggi.70046. Epub 2025 Apr 14. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2025. PMID: 40229144 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Factors Contributing to the Diabetes Burden in the Elderly: A Clinical Perspective.Scand J Caring Sci. 2025 Jun;39(2):e70032. doi: 10.1111/scs.70032. Scand J Caring Sci. 2025. PMID: 40405329 Free PMC article.
-
In-Hospital Management of Hyperglycemia: The Role of Insulin Degludec.Diabetes Ther. 2025 Apr;16(4):547-568. doi: 10.1007/s13300-025-01707-w. Epub 2025 Feb 27. Diabetes Ther. 2025. PMID: 40014293 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Morley JE. The elderly type 2 diabetic patient: Special considerations. Diabet Med 1998; 15(Suppl 4): S41–S46. - PubMed
-
- Cho NH, Shaw JE, Karuranga S, et al. IDF diabetes atlas: Global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2017 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2018; 138: 271–281. - PubMed
-
- Christiaens A, Henrard S, Zerah L, et al. Individualisation of glycaemic management in older people with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review of clinical practice guidelines recommendations. Age Ageing 2021; 50: 1935–1942. - PubMed
-
- Marengoni A, Angleman S, Melis R, et al. Aging with multimorbidity: A systematic review of the literature. Ageing Res Rev 2011; 10: 430–439. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical