Detection of soil-transmitted helminths and Schistosoma spp. by nucleic acid amplification test: Results of the first 5 years of the only international external quality assessment scheme
- PMID: 39116195
- PMCID: PMC11335160
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0012404
Detection of soil-transmitted helminths and Schistosoma spp. by nucleic acid amplification test: Results of the first 5 years of the only international external quality assessment scheme
Abstract
Background: Infections with soil-transmitted helminths (STH) and schistosomiasis (SCH) result in a significant global health burden, particularly in rural communities in low and middle-income countries. While microscopy remains the primary diagnostic method for STH and SCH in resource-limited settings, nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs) are gaining prominence as tools for evaluation of public health control programs in endemic countries, and individual diagnosis in high-income countries. Despite the high sensitivity and specificity of NAATs, previous research has highlighted inter-laboratory variations, both in technical and clinical performance, justifying the need for continuous proficiency testing.
Methodology: Results from 5 rounds over a 5-year period of the so far only longitudinal international Helminth External Molecular Quality Assessment Scheme (HEMQAS), coordinated by the Dutch Foundation for Quality Assessment in Medical Laboratories (SKML), were examined in order to (i) assess the diagnostic proficiency of laboratories in detecting helminths in stool and (ii) identify potential factors contributing to variations in performance.
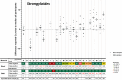
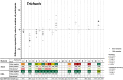
Outcome and conclusions: Thirty-six laboratories, from 18 countries and 5 continents, participated in HEMQAS. The overall diagnostic performances were satisfying, with remarkably low numbers (<2%) of false-positive results. False-negative results were more often reported for stool (15%) than for DNA (5%) samples. False-negative results varied largely between targets (the highest number (29%) for Trichuris trichiura). Twenty-five laboratories provided a sufficient number of results for a robust comparison between participating laboratories, which confirmed substantial inter-laboratory variability in quantitative NAAT results (Cq-values). This variability likely arises from differences in pre-treatment, DNA isolation and DNA-target amplification procedures. This study emphasizes the complexity of molecular diagnosis for STH and SCH, highlighting the critical role of proper stool preparation and DNA isolation methods. The results underscore the necessity for laboratory professionals and public health decision-makers to recognize these complexities and continuously undertake external quality assessment schemes to ensure accurate and reliable performance in molecular diagnosis.
Copyright: This is an open access article, free of all copyright, and may be freely reproduced, distributed, transmitted, modified, built upon, or otherwise used by anyone for any lawful purpose. The work is made available under the Creative Commons CC0 public domain dedication.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- Disease GBD, Injury I, Prevalence C. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2018;392(10159):1789–858. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32279-7 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- IHME. Schistosomiasis Level 3 cause 2023. [updated 2019; cited 2023 21-11-2023]. Available from: https://www.healthdata.org/results/gbd_summaries/2019/schistosomiasis-le....
-
- WHO. 2030 targets for soil-transmitted helminthiases control programmes 2020. [updated 2020; cited 2023 21-11-2023]. Available from: https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/330611/9789240000315-eng.pdf....
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

