Discovery of Selective Inhibitors for the Lysosomal Parkinson's Disease Channel TMEM175
- PMID: 39116214
- PMCID: PMC11513884
- DOI: 10.1021/jacs.4c05623
Discovery of Selective Inhibitors for the Lysosomal Parkinson's Disease Channel TMEM175
Abstract
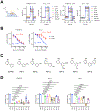
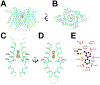
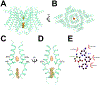
TMEM175 is a lysosomal potassium and proton channel that is associated with the development of Parkinson's disease. Advances in understanding the physiological roles of TMEM175 have been hampered by the absence of selective inhibitors, and studies involving genetic perturbations have yielded conflicting results. Here, we report the discovery and characterization of the first reported TMEM175-selective inhibitors, 2-phenylpyridin-4-ylamine (2-PPA), and AP-6. Cryo-EM structures of human TMEM175 bound by 2-PPA and AP-6 reveal that they act as pore blockers, binding at distinct sites in the pore and occluding the ion permeation pathway. Acute inhibition of TMEM175 by 2-PPA or AP-6 increases the level of lysosomal macromolecule catabolism, thereby accelerating macropinocytosis and other digestive processes. These inhibitors may serve as valuable tools to study the roles of TMEM175 in regulating lysosomal function and provide useful templates for future therapeutic development in Parkinson's disease.
Figures


References
-
- Jinn S; Drolet RE; Cramer PE; Wong AH; Toolan DM; Gretzula CA; Voleti B; Vassileva G; Disa J; Tadin-Strapps M; et al. TMEM175 deficiency impairs lysosomal and mitochondrial function and increases alpha-synuclein aggregation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2017, 114 (9), 2389–2394. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1616332114. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

