Regulation of the hematopoietic stem cell pool by C-Kit-associated trogocytosis
- PMID: 39116219
- PMCID: PMC11533977
- DOI: 10.1126/science.adp2065
Regulation of the hematopoietic stem cell pool by C-Kit-associated trogocytosis
Abstract
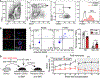
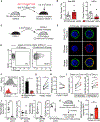
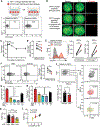
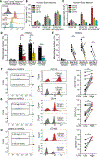
Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) are routinely mobilized from the bone marrow (BM) to the blood circulation for clinical transplantation. However, the precise mechanisms by which individual stem cells exit the marrow are not understood. This study identified cell-extrinsic and molecular determinants of a mobilizable pool of blood-forming stem cells. We found that a subset of HSCs displays macrophage-associated markers on their cell surface. Although fully functional, these HSCs are selectively niche-retained as opposed to stem cells lacking macrophage markers, which exit the BM upon forced mobilization. Macrophage markers on HSCs could be acquired through direct transfer by trogocytosis, regulated by receptor tyrosine-protein kinase C-Kit (CD117), from BM-resident macrophages in mouse and human settings. Our study provides proof of concept that adult stem cells utilize trogocytosis to rapidly establish and activate function-modulating molecular mechanisms.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DK112976/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL069438/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 CA253127/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL157948/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA230756/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK056638/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK116312/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- F32 HL158084/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DK137045/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL144456/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DK131401/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

