AI hybrid survival assessment for advanced heart failure patients with renal dysfunction
- PMID: 39117613
- PMCID: PMC11310499
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-50415-9
AI hybrid survival assessment for advanced heart failure patients with renal dysfunction
Abstract
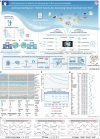
Renal dysfunction (RD) often characterizes the worse course of patients with advanced heart failure (AHF). Many prognosis assessments are hindered by researcher biases, redundant predictors, and lack of clinical applicability. In this study, we enroll 1736 AHF/RD patients, including data from Henan Province Clinical Research Center for Cardiovascular Diseases (which encompasses 11 hospital subcenters), and Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center. We developed an AI hybrid modeling framework, assembling 12 learners with different feature selection paradigms to expand modeling schemes. The optimized strategy is identified from 132 potential schemes to establish an explainable survival assessment system: AIHFLevel. The conditional inference survival tree determines a probability threshold for prognostic stratification. The evaluation confirmed the system's robustness in discrimination, calibration, generalization, and clinical implications. AIHFLevel outperforms existing models, clinical features, and biomarkers. We also launch an open and user-friendly website www.hf-ai-survival.com , empowering healthcare professionals with enhanced tools for continuous risk monitoring and precise risk profiling.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Clinical Implications of Serum Albumin Levels in Acute Heart Failure: Insights From DOSE-AHF and ROSE-AHF.J Card Fail. 2016 Nov;22(11):884-890. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2016.01.015. Epub 2016 Feb 2. J Card Fail. 2016. PMID: 26844764 Free PMC article.
-
A combined-biomarker approach to clinical phenotyping renal dysfunction in heart failure.J Card Fail. 2014 Dec;20(12):912-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2014.08.008. Epub 2014 Aug 23. J Card Fail. 2014. PMID: 25152498 Free PMC article.
-
Implications of Alternative Hepatorenal Prognostic Scoring Systems in Acute Heart Failure (from DOSE-AHF and ROSE-AHF).Am J Cardiol. 2017 Jun 15;119(12):2003-2009. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2017.03.031. Epub 2017 Mar 29. Am J Cardiol. 2017. PMID: 28433216 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Artificial intelligence-enhanced electrocardiography for accurate diagnosis and management of cardiovascular diseases.J Electrocardiol. 2024 Mar-Apr;83:30-40. doi: 10.1016/j.jelectrocard.2024.01.006. Epub 2024 Jan 28. J Electrocardiol. 2024. PMID: 38301492 Review.
-
Advanced Heart Failure Therapies and Cardiorenal Syndrome.Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2018 Sep;25(5):443-453. doi: 10.1053/j.ackd.2018.08.012. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2018. PMID: 30309462 Review.
Cited by
-
A physics-informed and data-driven framework for robotic welding in manufacturing.Nat Commun. 2025 May 23;16(1):4807. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-60164-y. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40410176 Free PMC article.
-
AI-based Assessment of Risk Factors for Coronary Heart Disease in Patients With Diabetes Mellitus and Construction of a Prediction Model for a Treatment Regimen.Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2025 Jun 25;26(6):36293. doi: 10.31083/RCM36293. eCollection 2025 Jun. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2025. PMID: 40630462 Free PMC article.
-
Association of platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio with 1-year all-cause mortality in ICU patients with heart failure.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 30;14(1):32016. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-83583-1. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39738748 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

