Nivolumab plus platinum-doublet chemotherapy in treatment-naive patients with advanced grade 3 Neuroendocrine Neoplasms of gastroenteropancreatic or unknown origin: The multicenter phase 2 NICE-NEC trial (GETNE-T1913)
- PMID: 39117670
- PMCID: PMC11310219
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-50969-8
Nivolumab plus platinum-doublet chemotherapy in treatment-naive patients with advanced grade 3 Neuroendocrine Neoplasms of gastroenteropancreatic or unknown origin: The multicenter phase 2 NICE-NEC trial (GETNE-T1913)
Abstract
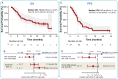
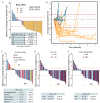
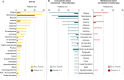
The prognosis of patients with advanced high-grade (G3) digestive neuroendocrine neoplasms (NENs) is rather poor. The addition of immune checkpoint inhibition to platinum-based chemotherapy may improve survival. NICE-NEC (NCT03980925) is a single-arm, phase II trial that recruited chemotherapy-naive, unresectable advanced or metastatic G3 NENs of gastroenteropancreatic (GEP) or unknown origin. Patients received nivolumab 360 mg intravenously (iv) on day 1, carboplatin AUC 5 iv on day 1, and etoposide 100 mg/m2/d iv on days 1-3, every 3 weeks for up to six cycles, followed by nivolumab 480 mg every 4 weeks for up to 24 months, disease progression, death or unacceptable toxicity. The primary endpoint was the 12-month overall survival (OS) rate (H0 50%, H1 72%, β 80%, α 5%). Secondary endpoints were objective response rate (ORR), duration of response (DoR), progression-free survival (PFS), and safety. From 2019 to 2021, 37 patients were enrolled. The most common primary sites were the pancreas (37.8%), stomach (16.2%) and colon (10.8%). Twenty-five patients (67.6%) were poorly differentiated carcinomas (NECs) and/or had a Ki67 index >55%. The ORR was 56.8%. Median PFS was 5.7 months (95%CI: 5.1-9) and median OS 13.9 months (95%CI: 8.3-Not reached), with a 12-month OS rate of 54.1% (95%CI: 40.2-72.8) that did not meet the primary endpoint. However, 37.6% of patients were long-term survivors (>2 years). The safety profile was consistent with previous reports. There was one treatment-related death. Nivolumab plus platinum-based chemotherapy was associated with prolonged survival in over one-third of chemonaïve patients with G3 GEP-NENs, with a manageable safety profile.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
RGC has received honoraria for speaker engagements, advisory roles or funding for continuous medical education from AAA, Advanz Pharma, Amgen, Astellas, Bayer, BMS, Boerhringer, Esteve, GSK, Hutchmed, Ipsen, Midatech Pharma, MSD, Novartis, PharmaMar, Servier, Takeda, and has received research support from Pfizer, BMS and MSD. EG has received honoraria for speaker engagements, advisory roles or funding of continuous medical education from Adacap, AMGEN, Angelini, Astellas, Astra Zeneca, Bayer, Blueprint, Bristol Myers Squibb, Caris Life Sciences, Celgene, Clovis-Oncology, Eisai, Eusa Pharma, Genetracer, Guardant Health, HRA-Pharma, IPSEN, ITM-Radiopharma, Janssen, Lexicon, Lilly, Merck KGaA, MSD, Nanostring Technologies, Natera, Novartis, ONCODNA (Biosequence), Palex, Pharmamar, Pierre Fabre, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi-Genzyme, Servier, Taiho, and Thermo Fisher Scientific. EG has received research grants from Pfizer, Astra Zeneca, Astellas, and Lexicon Pharmaceuticals. TA-G declares participating in advisory boards for Astellas, Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, EISAI, IPSEN, Lilly, Novartis Advanced Accelerator Applications, Pfizer, Roche, and Sanofi; act as invited speaker for Janssen-Cilag; and being project lead for Johnson & Johnson, IPSEN and Pfizer. JC declares scientific consultancy role (speaker and advisory roles) for Novartis, Pfizer, Ipsen, Exelixis, Bayer, Eisai, Advanced Accelerator Applications, Amgen, Sanofi, Lilly, Hudchmed, ITM, Merck Serono, Roche, Esteve, Advanz; and received research grants from Novartis, Pfizer, Astrazeneca, Advanced Accelerator Applications, Eisai, Amgen, ITM and Bayer. PJ-F has provided scientific advice and/or received honoraria from Astellas, BMS, Eisai, Lilly, MSD, Pfizer and Rovi. IS received payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers bureaus, manuscript writing or educational events from AAA, Novartis, Pharmamar, Ipsen, Pfizer, Amgen,Bayer; support for attending meetings and/or travel from AAA, Novartis, Pharmamar, Ipsen, Boehringer, Advanz Pharma, Esteve Pharmaceuticals, Amgen, Bayer; and participated on a Data Safety Monitoring Board or Advisory Board for AAA, Novartis, Pharmamar, Ipsen, Boehringer, Advanz Pharma, Esteve Pharmaceuticals, Amgen, Bayer. AT received support for attending meetings and /or travel from MSD, Roche; received payment honoraria for lectures/scientific advice from Pfizer and Diaceutics; and working as an employee at MD Anderson Hospital. All the remaining co-authors state that they do not have conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Garcia-Carbonero, R. et al. ENETS consensus guidelines for high-grade gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors and neuroendocrine carcinomas. Neuroendocrinology. 10.1159/000443172 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Pavel, M. et al. Gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 10.1016/j.annonc.2020.03.304 (2020). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

