Current best practices and future opportunities for reproducible findings using large-scale neuroimaging in psychiatry
- PMID: 39117903
- PMCID: PMC11526024
- DOI: 10.1038/s41386-024-01938-8
Current best practices and future opportunities for reproducible findings using large-scale neuroimaging in psychiatry
Erratum in
-
Correction: Neuropsychopharmacology Volume 50 Issue 1.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2025 May;50(6):1019-1020. doi: 10.1038/s41386-025-02087-2. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2025. PMID: 40108440 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
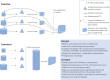
Research into the brain basis of psychopathology is challenging due to the heterogeneity of psychiatric disorders, extensive comorbidities, underdiagnosis or overdiagnosis, multifaceted interactions with genetics and life experiences, and the highly multivariate nature of neural correlates. Therefore, increasingly larger datasets that measure more variables in larger cohorts are needed to gain insights. In this review, we present current "best practice" approaches for using existing databases, collecting and sharing new repositories for big data analyses, and future directions for big data in neuroimaging and psychiatry with an emphasis on contributing to collaborative efforts and the challenges of multi-study data analysis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Szucs D, Ioannidis JP. Sample size evolution in neuroimaging research: An evaluation of highly-cited studies (1990-2012) and of latest practices (2017-2018) in high-impact journals. Neuroimage. 2020;221:117164. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

