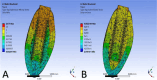
A forecasting model for suitable dental implantation in canine mandibular premolar region based on finite element analysis
- PMID: 39118061
- PMCID: PMC11308459
- DOI: 10.1186/s12917-024-04221-6
A forecasting model for suitable dental implantation in canine mandibular premolar region based on finite element analysis
Abstract
In recent years, dental implants have become a trend in the treatment of human patients with missing teeth, which may also be an acceptable method for companion animal dentistry. However, there is a gap challenge in determining appropriate implant sizes for different dog breeds and human. In this study, we utilized skull computed tomography data to create three-dimensional models of the mandibles of dogs in different sizes. Subsequently, implants of various sizes were designed and subjected to biomechanical finite element analysis to determine the optimal implant size. Regression models were developed, exploring the relationship between the average weight of dogs and the size of premolar implants. Our results illustrated that the regression equations for mean body weight (x, kg) and second premolar (PM2), third premolar (PM3), and fourth premolar (PM4) implant length (y, mm) in dogs were: y = 0.2785x + 7.8209, y = 0.2544x + 8.9285, and y = 0.2668x + 10.652, respectively; the premolar implant diameter (mm) y = 0.0454x + 3.3506, which may provide a reference for determine suitable clinical implant sizes for dogs.
Keywords: Companion animal dentistry; Computed tomography; Computer-aided design; Dental implantation; Finite element analysis; Implant; Premolar teeth.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Biomechanics of Dental Implantation in the Giant Panda (Ailuropoda melanoleuca): A Comparative Study Using Finite Element Analysis.J Vet Dent. 2025 Jul;42(4):273-280. doi: 10.1177/08987564241265420. Epub 2024 Jul 23. J Vet Dent. 2025. PMID: 39042890
-
[Analysis of the effect of mesial implant position on surrounding bone stress of mandibular edentulous jaw under dynamic loads].Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2017 Nov 9;52(11):672-677. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1002-0098.2017.11.005. Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 29972946 Chinese.
-
Characterization of the Correct Mandibular Premolar Region for Delayed Dental Implantation in Beagle Dogs.J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 2018 May 1;57(3):302-307. doi: 10.30802/AALAS-JAALAS-17-000155. Epub 2018 Apr 12. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 2018. PMID: 29734971 Free PMC article.
-
[Three-dimensional finite element analysis of the effect of the location and diameter of implants on the stress distribution in three-unit implant-supported posterior cantilever fixed partial dentures under dynamic loads].Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2013 Dec;31(6):552-6. Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 24437284 Chinese.
-
Finite element stress analysis of cuneiform and cylindrical threaded implant geometries.Technol Health Care. 2006;14(4-5):421-38. Technol Health Care. 2006. PMID: 17065763 Review.
Cited by
-
Finite Element Analysis of Stress Distribution in Canine Lumbar Fractures with Different Pedicle Screw Insertion Angles.Vet Sci. 2025 Jul 19;12(7):682. doi: 10.3390/vetsci12070682. Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40711342 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating the concept of three-dimensional printing guided endodontics in the dog.Front Vet Sci. 2024 Nov 21;11:1481612. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1481612. eCollection 2024. Front Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 39641096 Free PMC article.
-
Primary Evaluation of Three-Dimensional Printing-Guided Endodontics in the Dog Maxillary.Vet Sci. 2025 Jul 14;12(7):665. doi: 10.3390/vetsci12070665. Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40711325 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous