The right ventricular dysfunction and ventricular interdependence in patients with T2DM and aortic regurgitation: an assessment using CMR feature tracking
- PMID: 39118075
- PMCID: PMC11312922
- DOI: 10.1186/s12933-024-02372-2
The right ventricular dysfunction and ventricular interdependence in patients with T2DM and aortic regurgitation: an assessment using CMR feature tracking
Abstract
Background: Patients with concomitant type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and aortic regurgitation (AR) can present with right ventricular (RV) dysfunction. The current study aimed to evaluate the impact of AR on RV impairment and the importance of ventricular interdependence using cardiac magnetic resonance feature tracking (CMR‑FT) in patients with T2DM.
Methods: This study included 229 patients with T2DM (AR-), 88 patients with T2DM (AR+), and 122 healthy controls. The biventricular global radial strain (GRS), global circumferential strain (GCS), and global longitudinal peak strain (GLS) were calculated with CMR‑FT and compared among the healthy control, T2DM (AR-), and T2DM (AR+) groups. The RV regional strains at the basal, mid, and apical cavities between the T2DM (AR+) group and subgroups with different AR degrees were compared. Backward stepwise multivariate linear regression analyses were performed to determine the effects of AR and left ventricular (LV) strains on RV strains.
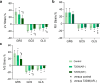
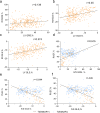
Results: The RV GLS, LV GRS, LV GCS, LV GLS, interventricular septal (IVS) GRS and IVS GCS were decreased gradually from the controls through the T2DM (AR-) group to the T2DM (AR+) group. The IVS GLS of the T2DM (AR-) and T2DM (AR+) groups was lower than that of the control group. AR was independently associated with LV GRS, LV GCS, LV GLS, RV GCS, and RV GLS. If AR and LV GLSs were included in the regression analyses, AR and LV GLS were independently associated with RV GLS.
Conclusion: AR can exacerbate RV dysfunction in patients with T2DM, which may be associated with the superimposed strain injury of the left ventricle and interventricular septum. The RV longitudinal and circumferential strains are important indicators of cardiac injury in T2DM and AR. The unfavorable LV-RV interdependence supports that while focusing on improving LV function, RV dysfunction should be monitored and treated in order to slow the progression of the disease and the onset of adverse outcomes.
Keywords: Aortic regurgitation; CMR feature‑tracking; Right ventricle; Strain; Type 2 diabetes mellitus; Ventricular interdependence.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of T2DM on right ventricular systolic dysfunction and interventricular interactions in patients with essential hypertension: evaluation using CMR tissue tracking.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2022 Nov 9;21(1):238. doi: 10.1186/s12933-022-01678-3. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2022. PMID: 36352469 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of diabetes mellitus on right ventricular dysfunction and ventricular interdependence in hypertensive patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction assessed via 3.0 T cardiac MRI.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024 Oct 23;23(1):375. doi: 10.1186/s12933-024-02472-z. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024. PMID: 39443983 Free PMC article.
-
Early detection of left atrial and bi-ventricular myocardial strain abnormalities by MRI feature tracking in normotensive or hypertensive T2DM patients with preserved LV function.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2020 Apr 23;20(1):196. doi: 10.1186/s12872-020-01469-2. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2020. PMID: 32326882 Free PMC article.
-
Myocardial Strain Measurements Derived From MR Feature-Tracking: Influence of Sex, Age, Field Strength, and Vendor.JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2024 Apr;17(4):364-379. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2023.05.019. Epub 2023 Jul 19. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2024. PMID: 37480906
-
A Comprehensive Review of Two-Dimensional Speckle-Tracking Echocardiography in Assessing Right and Left Ventricular Function in Diabetic Patients.Clin Cardiol. 2025 May;48(5):e70153. doi: 10.1002/clc.70153. Clin Cardiol. 2025. PMID: 40405445 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of diabetes mellitus on myocardial function and clinical outcomes in patients with significant aortic regurgitation.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025 Jul 15;24(1):290. doi: 10.1186/s12933-025-02843-0. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025. PMID: 40665315 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Galusko V, Thornton G, Jozsa C, Sekar B, Aktuerk D, Treibel TA, Petersen SE, Ionescu A, Ricci F, Khanji MY. Aortic regurgitation management: a systematic review of clinical practice guidelines and recommendations. Eur Heart J Qual Care Clin Outcomes. 2022;8:113–26. 10.1093/ehjqcco/qcac001 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

