Characterization of GQA as a novel β-lactamase inhibitor of CTX-M-15 and KPC-2 enzymes
- PMID: 39118086
- PMCID: PMC11308155
- DOI: 10.1186/s12934-024-02421-1
Characterization of GQA as a novel β-lactamase inhibitor of CTX-M-15 and KPC-2 enzymes
Abstract
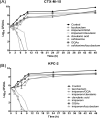
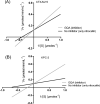
β-lactam resistance is a significant global public health issue. Outbreaks of bacteria resistant to extended-spectrum β-lactams and carbapenems are serious health concerns that not only complicate medical care but also impact patient outcomes. The primary objective of this work was to express and purify two soluble recombinant representative serine β‑lactamases using Escherichia coli strain as an expression host and pET101/D as a cloning vector. Furthermore, a second objective was to evaluate the potential, innovative, and safe use of galloylquinic acid (GQA) from Copaifera lucens as a potential β-lactamase inhibitor.In the present study, blaCTX-M-15 and blaKPC-2 represented genes encoding for serine β-lactamases that were cloned from parent isolates of E. coli and K. pneumoniae, respectively, and expression as well as purification were performed. Moreover, susceptibility results demonstrated that recombinant cells became resistant to all test carbapenems (MICs; 64-128 µg/mL) and cephalosporins (MICs; 128-512 µg/mL). The MICs of the tested β-lactam antibiotics were determined in combination with 4 µg/mL of GQA, clavulanic acid, or tazobactam against E. coli strains expressing CTX-M-15 or KPC-2-β-lactamases. Interestingly, the combination with GQA resulted in an important reduction in the MIC values by 64-512-fold to the susceptible range with comparable results for other reference inhibitors. Additionally, the half-maximal inhibitory concentration of GQA was determined using nitrocefin as a β-lactamase substrate. Data showed that the test agent was similar to tazobactam as an efficient inhibitors of the test enzymes, recording smaller IC50 values (CTX-M-15; 17.51 for tazobactam, 28.16 µg/mL for GQA however, KPC-2; 20.91 for tazobactam, 24.76 µg/mL for GQA) compared to clavulanic acid. Our work introduces GQA as a novel non-β-lactam inhibitor, which interacts with the crucial residues involved in β-lactam recognition and hydrolysis by non-covalent interactions, complementing the enzyme's active site. GQA markedly enhanced the potency of β-lactams against carbapenemase and extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing strains, reducing the MICs of β-lactams to the susceptible range. The β-lactamase inhibitory activity of GQA makes it a promising lead molecule for the development of more potent β-lactamase inhibitors.
Keywords: Escherichia coli; Klebsiella pneumoniae; Carbapenemase; Extended-spectrum β-lactamases; Galloylquinic acid; β-lactamase inhibitor.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors confirm the absence of competing interests.
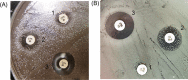
Figures



References
-
- Cruz-López F, Martínez-Meléndez A, Morfin-Otero R, Rodriguez-Noriega E, Maldonado-Garza HJ, Garza-González E. Efficacy and in vitro activity of novel antibiotics for infections with carbapenem-resistant gram-negative pathogens. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022;12:884365. 10.3389/fcimb.2022.884365. 10.3389/fcimb.2022.884365 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

