Uncovering the hidden socioeconomic impact of juvenile idiopathic arthritis and paving the way for other rare childhood diseases: an international, cross-disciplinary, patient-centered approach (PAVE Consortium)
- PMID: 39118107
- PMCID: PMC11312924
- DOI: 10.1186/s12969-024-01012-z
Uncovering the hidden socioeconomic impact of juvenile idiopathic arthritis and paving the way for other rare childhood diseases: an international, cross-disciplinary, patient-centered approach (PAVE Consortium)
Abstract
Background: Juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) refers to a heterogeneous group of rheumatic conditions in children. Novel drugs have greatly improved disease outcomes; however, outcomes are impacted by limited awareness of the importance of early diagnosis and adequate treatment, and by differences in access across health systems. As a result, patients with JIA continue to be at risk for short- and long-term morbidity, as well as impacts on virtually all aspects of life of the child and family.
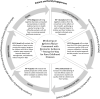
Main body: Literature on the socioeconomic burden of JIA is largely focused on healthcare costs, and the impact of JIA on patients, families, and communities is not well understood. High quality evidence on the impact of JIA is needed to ensure that patients are receiving necessary support, timely diagnostics, and adequate treatment, and to inform decision making and resource allocation. This commentary introduces the European Joint Programme on Rare Diseases: Producing an Arthritis Value Framework with Economic Evidence: Paving the Way for Rare Childhood Diseases (PAVE) project, which will co-develop a patient-informed value framework to measure the impact of JIA on individuals and on society. With a patient-centered approach, fundamental to PAVE is the involvement of three patient advocacy organizations from Canada, Israel, and Europe, as active research partners co-designing all project phases and ensuring robust patient and family engagement. The framework will build on the findings of projects from six countries: Canada, Germany, Switzerland, Spain, Israel, and Belgium, exploring costs, outcomes (health, well-being), and unmet needs (uveitis, mental health, equity).
Conclusion: This unique international collaboration will combine evidence on costs (from family to societal), outcomes (clinical, patient and family outcomes), and unmet needs, to co-design and build a framework with patients and families to capture the full impact of JIA. The framework will support the development of high-quality evidence, encompassing economic and clinical considerations, unmet needs, and patient perspectives, to inform equitable resource allocation, health system planning, and quality of care better aligned with the needs of children with JIA, their families, and communities. Knowledge gained from this novel approach may pave the way forward to be applied more broadly to other rare childhood diseases.
Keywords: Childhood Arthritis; International collaboration; Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis; Participatory research; Patient-centered research; Patient-partnered research; Rare disease; Socioeconomic burden.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Hayeems RZ, Michaels-Igbokwe C, Venkataramanan V, Hartley T, Acker M, Gillespie M, et al. The complexity of diagnosing rare disease: an organizing framework for outcomes research and health economics based on real-world evidence. Genet Med. 2022;24(3):694–702. 10.1016/j.gim.2021.11.005. 10.1016/j.gim.2021.11.005 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rare Diseases at FDA | FDA. Available from: https://www.fda.gov/patients/rare-diseases-fda. [cited 2023 Jan 26].
-
- Health Canada. Building a national strategy for high-cost drugs for rare diseases: a discussion paper for engaging Canadians. 2021. Available from: https://epe.lac-bac.gc.ca/100/201/301/weekly_acquisitions_list-ef/2021/2.... [cited 2022 Feb 27].
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials