Anti-Helicobacter pylori Infection Treatment and Pulmonary Hypersensitivity: Case Series and Review of the Literature
- PMID: 39118282
- PMCID: PMC11310268
- DOI: 10.1111/crj.13816
Anti-Helicobacter pylori Infection Treatment and Pulmonary Hypersensitivity: Case Series and Review of the Literature
Abstract
Background: Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection is currently widespread throughout the world. Bismuth-containing quadruple therapy is widely used, but it has rarely been associated with interstitial lung disease.
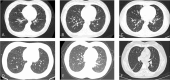
Case presentation: We described six cases with similar clinical symptoms and typical pulmonary interstitial imaging changes during anti-H. pylori therapy, usually on Days 7-12 following treatment. Anti-H. pylori infection treatment was discontinued when it was suspected to be the cause of the clinical symptoms, and all of the patients accepted observation therapy. All of them had a favorable outcome, the clinical symptoms returned to normal almost 1 week later, and the chest computed tomography (CT) scan images showed remarkable absorption 4 weeks later.
Conclusions: Drug interactions could be the cause, and the most likely drug was furazolidone. All of the patients recovered quickly after drug discontinuation, and low-dose steroid may help shorten the recovery time.
Keywords: anti‐H. pylori infection treatment; bismuth‐containing quadruple therapy; furazolidone; interstitial lung disease; pulmonary hypersensitivity.
© 2024 The Author(s). The Clinical Respiratory Journal published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

