Sex differences in the impact of frailty on patients with heart failure: A retrospective cohort study
- PMID: 39118410
- PMCID: PMC11631316
- DOI: 10.1002/ehf2.14938
Sex differences in the impact of frailty on patients with heart failure: A retrospective cohort study
Abstract
Aims: Limited literature shows the existence of sex differences in the long-term prognosis of heart failure (HF) patients with frailty. In this study, whether sex differences exist in the impact of frailty on death from cardiovascular causes in patients with HF was investigated by conducting a retrospective cohort study.
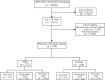
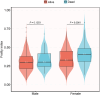
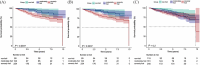
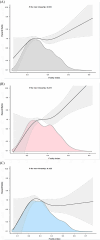
Methods and results: Data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) study (2009-2018) were used to conduct a retrospective cohort study of 958 participants with HF. Patients were grouped based on sex and frailty index (FI). The relationship between death from cardiovascular causes and baseline frailty was assessed by Cox proportional hazard analysis and the Kaplan-Meier (K-M) plot. The study population had an age of 67.3 ± 12.3. Among them, around 54.5% were male. A median follow-up of 3.6 years was performed. After that, females who died from cardiovascular causes exhibited higher baseline FI values, while males did not show this trend (P < 0.05; P = 0.1253). Cox regression analysis demonstrated a significant association between FI and cardiovascular mortality in females (most frail: hazard ratio (HR) = 3.65, 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.07 ~ 12.39, P < 0.05; per 1-unit increase in FI: HR = 1.78, 95% CI: 1.33 ~ 2.39, P < 0.001). A dose-response association between FI and cardiovascular mortality was presented by restricted cubic splines.
Conclusions: Frailty is related to an increased risk of cardiovascular mortality in HF patients, particularly female patients.
Keywords: Cardiovascular death; Frailty index; Heart failure; Sex differences.
© 2024 The Author(s). ESC Heart Failure published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Society of Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

