Targeted Therapy with a Novel Superantigen-based Fusion Protein Against Interleukin-13 Receptor α2-overexpressing Tumor Cells: An In-silico Study
- PMID: 39118800
- PMCID: PMC11304462
- DOI: 10.30699/IJP.2024.2014231.3200
Targeted Therapy with a Novel Superantigen-based Fusion Protein Against Interleukin-13 Receptor α2-overexpressing Tumor Cells: An In-silico Study
Abstract
Background & objective: Superantigens are bacterial toxins that induce a massive immune response in the host. Superantigen staphylococcal enterotoxin B (SEB) can form a ternary complex with its receptors, MHC class II (MHCII) and TCR, and can be used in tumor-targeting therapy, particularly when cooperating with a specific vector. In this study, SEB was fused to interleukin-13 (IL13), which forms a complex with IL13 receptor α2 (IL13Rα2) overexpressed in glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) cells for therapeutic goals.
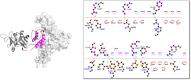
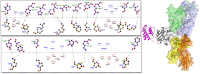
Methods: We designed four fusion proteins based on the arrangement of SEB (N- or C-terminal domain) and provided a flexible inter-domain linker (no or yes), resulting in the formation of SEB-IL13, SEB-L-IL13, IL13-SEB, and IL13-L-SEB, respectively. These fusion proteins were then evaluated for their various physicochemical properties and structural characteristics. Bioinformatics tools were employed to predict, refine, and validate the three-dimensional structure of the fusion proteins. In addition, the fusion proteins were docked with IL13Rα2, MHCII, and TCR receptors through the HADDOCK 2.4 server. The candidate fusion protein was subjected to molecular dynamics simulation.
Results: There were differences among the designed fusion proteins. The model with the N-terminal domain of IL13 and containing an inter-domain linker (IL13-L-SEB) was stable and had a long half-life. The docking analysis revealed that the IL13-L-SEB fusion protein had a higher binding affinity to the IL13Rα2, MHCII, and TCR receptors. Finally, using molecular dynamics simulation through iMODS, acceptable results were obtained for the IL13-L-SEB docked complexes.
Conclusion: The results suggest IL13-L-SEB is a promising novel fusion protein for cancer therapeutic application.
Keywords: Fusion protein; Glioblastoma multiforme; Interleukin-13; Molecular docking; Staphylococcal enterotoxin B..
© 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Xu S, Tang L, Li X, Fan F, Liu Z. Immunotherapy for glioma: current management and future application. Cancer Lett. 2020 Apr;476:1–2. - PubMed
-
- Debinski W, Gibo DM, Hulet SW, Connor JR, Gillespie GY. The receptor for interleukin 13 is a marker and therapeutic target for human high-grade gliomas. Clin Cancer Res. 1999;5(5):985–90. - PubMed
-
- Husain SR, Puri RK. Interleukin-13 receptor-directed cytotoxin for malignant glioma therapy: from bench to bedside. Neuro Oncol. 2003;65:37–48. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
