Negative impact of nurses' fear of COVID-19: the moderating role of implementation of knowledge management
- PMID: 39118971
- PMCID: PMC11306124
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1426408
Negative impact of nurses' fear of COVID-19: the moderating role of implementation of knowledge management
Abstract
Background: During the COVID-19 pandemic, nurses encountered substantial infection risks and psychological strain, which severely affected their emotional well-being, professional attitudes, and job performance. This study investigated the impact of nurses' fear of COVID-19 on their intention to leave the occupation and emotional labor as well as the moderating role of the implementation of knowledge management on these primary variables.
Methods: To mitigate common method bias, this research adopted a two-phase questionnaire approach, targeting nurses at a medical center in central Taiwan. In the first phase, 300 copies of questionnaire were distributed for participants to complete self-assessment surveys covering fear of COVID-19, knowledge management implementation, and demographic information. After 1 month, the participants were invited to complete a follow-up questionnaire, focusing on the intention to leave the occupation and emotional labor. The questionnaire was conducted from June to July 2022. Through this two-phase distribution method, after exclusion of invalid responses, a total of 288 valid responses were collected, resulting in a response rate of 96%. The proposed hypotheses were verified using hierarchical regression conducted with SPSS version 25.0.
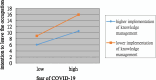
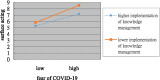
Results: The findings indicated that nurses' fear of COVID-19 was significantly and positively associated with their intention to leave the occupation and surface acting, but negatively associated with their deep acting. Moreover, the implementation of knowledge management significantly moderated the positive relationship among fear of COVID-19, intention to leave the occupation, and surface acting. A robust knowledge management system weakened the positive association among fear of COVID-19, intention to leave the occupation, and surface acting.
Conclusion: In summary, nurses' fear of COVID-19 may increase their tendency to leave the nursing profession and engage in more surface acting and less deep acting. However, effective knowledge management practices can mitigate these adverse effects. Hospitals can thus establish and employ comprehensive knowledge management systems to enhance nurses' resilience and help alleviate their fear of future pandemics and their potential negative repercussions.
Keywords: COVID-19; deep acting; emotional labor; fear; intention to leave the occupation; knowledge management; nurses; surface acting.
Copyright © 2024 Chu.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization . WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) dashboard. (2024). Available at: https://covid19.who.int/
-
- World Health Organization . The impact of COVID-19 on health and care workers: a closer look at deaths. (2021). Available at: https://iris.who.int/handle/10665/345300
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical