Mortality trends in people with disabilities before and during the COVID-19 pandemic in South Korea, 2017-2022
- PMID: 39118973
- PMCID: PMC11306165
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1414515
Mortality trends in people with disabilities before and during the COVID-19 pandemic in South Korea, 2017-2022
Abstract
Objective: To investigate temporal trends in mortality rates and underlying causes of death in persons with disabilities before and during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic.
Methods: Annual mortality rates and causes of death were analyzed using data covering the 2017-2022 period.
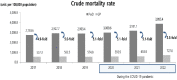
Results: The mortality rate among people with disabilities increased from 2017 to 2022; the rate was five times higher during COVID-19 in this population than in the general population. When analyzing the cause of death, the incidence of infectious diseases and tuberculosis decreased after COVID-19. In contrast, the incidence of other bacillary disorders (A30-A49) increased. The incidence of respiratory system diseases (J00-J99), influenza and pneumonia (J09-J18), and other acute lower respiratory infections (J20-J22) decreased before COVID-19, while the incidence of lung diseases due to external agents (J60-J70), other respiratory diseases principally affecting the interstitium (J80-J84), and other diseases of the pleura (J90-J94) increased during the pandemic. The risk of COVID-19 death among people with disabilities was 1.1-fold higher for female patients (95% CI = 1.06-1.142), 1.41-fold for patients aged 70 years and older (95% CI = 1.09-1.82), and 1.24-fold higher for people with severe disabilities (95% CI = 1.19-1.28).
Conclusions: The mortality rate in people with disabilities significantly increased during COVID-19, compared with that before the pandemic. People with disabilities had a higher mortality rate during COVID-19 compared with the general population. Risk factors must be reduced to prevent high mortality rates in this population.
Keywords: COVID-19; South Korea; infection; mortality; people with disability.
Copyright © 2024 Kim, Kim, Kwon, Kim, Kim and Ho.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization . General's statement on IHR Emergency Committee on Novel Coronavirus. (2019). Available online at: https://www.who.int/director-general/speeches/detail/who-director-genera... (accessed August 7, 2023).
-
- Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency (2020) . Current Status of Domestic Outbreak of COVID-19. Available online at: https://www.kdca.go.kr/board/board.es?mid=a20501010000&bid=0015&act=view... (accessed August 7, 2023).
-
- Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency . Social Distancing Adjustment Plan. (2023). Available online at: https://www.kdca.go.kr/board/board.es?mid=a20501020000&bid=0015&list_no=... (accessed August 7, 2023).
-
- Korean Culture and Information Service . Declaring the end of COVID-19… President Yoon “Restoration of daily life after 3 years and 4 months”. (2023). https://www.kocis.go.kr/koreanet/view.do?seq=1044801 (accessed August 7, 20230).
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

