Correction to "The neoteny goldilocks zone: The evolution of neoteny in Ambystoma"
- PMID: 39119177
- PMCID: PMC11306506
- DOI: 10.1002/ece3.70084
Correction to "The neoteny goldilocks zone: The evolution of neoteny in Ambystoma"
Abstract
[This corrects the article DOI: 10.1002/ece3.11240.].
© 2024 The Author(s). Ecology and Evolution published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
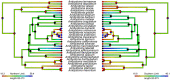
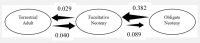
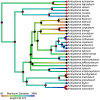

Erratum for
-
The neoteny goldilocks zone: The evolution of neoteny in Ambystoma.Ecol Evol. 2024 Apr 8;14(4):e11240. doi: 10.1002/ece3.11240. eCollection 2024 Apr. Ecol Evol. 2024. PMID: 38590547 Free PMC article.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

