Array tomography: trails to discovery
- PMID: 39119254
- PMCID: PMC11308915
- DOI: 10.1515/mim-2024-0001
Array tomography: trails to discovery
Abstract
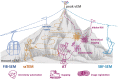
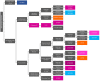
Tissue slicing is at the core of many approaches to studying biological structures. Among the modern volume electron microscopy (vEM) methods, array tomography (AT) is based on serial ultramicrotomy, section collection onto solid support, imaging via light and/or scanning electron microscopy, and re-assembly of the serial images into a volume for analysis. While AT largely uses standard EM equipment, it provides several advantages, including long-term preservation of the sample and compatibility with multi-scale and multi-modal imaging. Furthermore, the collection of serial ultrathin sections improves axial resolution and provides access for molecular labeling, which is beneficial for light microscopy and immunolabeling, and facilitates correlation with EM. Despite these benefits, AT techniques are underrepresented in imaging facilities and labs, due to their perceived difficulty and lack of training opportunities. Here we point towards novel developments in serial sectioning and image analysis that facilitate the AT pipeline, and solutions to overcome constraints. Because no single vEM technique can serve all needs regarding field of view and resolution, we sketch a decision tree to aid researchers in navigating the plethora of options available. Lastly, we elaborate on the unexplored potential of AT approaches to add valuable insight in diverse biological fields.
Keywords: ATUM; array tomography; light microscopy; serial sectioning; ultramicrotomy; volume electron microscopy.
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter on behalf of Thoss Media.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: KDM has founder’s equity interests in Aratome, LLC (Menlo Park, CA), an enterprise that produces array tomography materials and services. All other authors state no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Schalek R., et al. ATUM-based SEM for high-speed large-volume biological reconstructions. Microsc. Microanal. . 2012;18:572–3. doi: 10.1017/s1431927612004710. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
