Machine Learning Constructed Based on Patient Plaque and Clinical Features for Predicting Stent Malapposition: A Retrospective Study
- PMID: 39119892
- PMCID: PMC11310765
- DOI: 10.1002/clc.24332
Machine Learning Constructed Based on Patient Plaque and Clinical Features for Predicting Stent Malapposition: A Retrospective Study
Abstract
Background: Stent malapposition (SM) following percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) for myocardial infarction continues to present significant clinical challenges. In recent years, machine learning (ML) models have demonstrated potential in disease risk stratification and predictive modeling.
Hypothesis: ML models based on optical coherence tomography (OCT) imaging, laboratory tests, and clinical characteristics can predict the occurrence of SM.
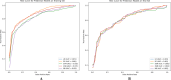
Methods: We studied 337 patients from the Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, China, who had PCI and coronary OCT from May to October 2023. We employed nested cross-validation to partition patients into training and test sets. We developed five ML models: XGBoost, LR, RF, SVM, and NB based on calcification features. Performance was assessed using ROC curves. Lasso regression selected features from 46 clinical and 21 OCT imaging features, which were optimized with the five ML algorithms.
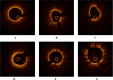
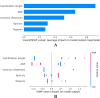
Results: In the prediction model based on calcification features, the XGBoost model and SVM model exhibited higher AUC values. Lasso regression identified five key features from clinical and imaging data. After incorporating selected features into the model for optimization, the AUC values of all algorithmic models showed significant improvements. The XGBoost model demonstrated the highest calibration accuracy. SHAP values revealed that the top five ranked features influencing the XGBoost model were calcification length, age, coronary dissection, lipid angle, and troponin.
Conclusion: ML models developed using plaque imaging features and clinical characteristics can predict the occurrence of SM. ML models based on clinical and imaging features exhibited better performance.
Keywords: acute myocardial infarction; machine learning; optical coherence tomography; percutaneous coronary intervention; stent malapposition.
© 2024 The Author(s). Clinical Cardiology published by Wiley Periodicals, LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Duggan J. P., Peters A. S., Trachiotis G. D., and Antevil J. L., “Epidemiology of Coronary Artery Disease,” Surgical Clinics of North America 102, no. 3 (2022): 499–516. - PubMed
-
- Zi Wei Z., Yuchen W., and Ben H., “STEMI Reperfusion Strategies for STEMI Patients: Advances in Comparative Studies Between Pharmacological Intervention and Primary PCI,” Chinese Journal of Cardiology 52, no. 03 (2024): 295–299.
-
- Holm N. R., Andreasen L. N., Neghabat O., et al., “OCT or Angiography Guidance for PCI in Complex Bifurcation Lesions,” New England Journal of Medicine 389, no. 16 (2023): 1477–1487. - PubMed
-
- Giustino G., Colombo A., Camaj A., et al., “Coronary In‐Stent Restenosis,” Journal of the American College of Cardiology 80, no. 4 (2022): 348–372. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

