Genomic Determinants of Outcome in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
- PMID: 39121442
- PMCID: PMC11458106
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.23.02238
Genomic Determinants of Outcome in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
Abstract
Purpose: Although cure rates for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) exceed 90%, ALL remains a leading cause of cancer death in children. Half of relapses arise in children initially classified with standard-risk (SR) disease.
Materials and methods: To identify genomic determinants of relapse in children with SR ALL, we performed genome and transcriptome sequencing of diagnostic and remission samples of children with SR (n = 1,381) or high-risk B-ALL with favorable cytogenetic features (n = 115) enrolled on Children's Oncology Group trials. We used a case-control study design analyzing 439 patients who relapsed and 1,057 who remained in complete remission for at least 5 years.
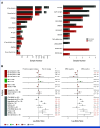
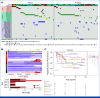
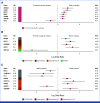
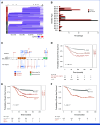
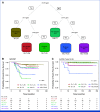
Results: Genomic subtype was associated with relapse, which occurred in approximately 50% of cases of PAX5-altered ALL (odds ratio [OR], 3.31 [95% CI, 2.17 to 5.03]; P = 3.18 × 10-8). Within high-hyperdiploid ALL, gain of chromosome 10 with disomy of chromosome 7 was associated with favorable outcome (OR, 0.27 [95% CI, 0.17 to 0.42]; P = 8.02 × 10-10; St Jude Children's Research Hospital validation cohort: OR, 0.22 [95% CI, 0.05 to 0.80]; P = .009), and disomy of chromosomes 10 and 17 with gain of chromosome 6 was associated with relapse (OR, 7.16 [95% CI, 2.63 to 21.51]; P = 2.19 × 10-5; validation cohort: OR, 21.32 [95% CI, 3.62 to 119.30]; P = .0004). Genomic alterations were associated with relapse in a subtype-dependent manner, including alterations of INO80 in ETV6::RUNX1 ALL, IKZF1, and CREBBP in high-hyperdiploid ALL and FHIT in BCR::ABL1-like ALL. Genomic alterations were also associated with the presence of minimal residual disease, including NRAS and CREBBP in high-hyperdiploid ALL.
Conclusion: Genetic subtype, patterns of aneuploidy, and secondary genomic alterations determine risk of relapse in childhood ALL. Comprehensive genomic analysis is required for optimal risk stratification.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00103285 NCT01190930 NCT00549848 NCT02883049 NCT00137111 NCT00075725.
Conflict of interest statement
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to
Open Payments is a public database containing information reported by companies about payments made to US-licensed physicians (
No other potential conflicts of interest were reported.
Figures

References
-
- Hunger SP, Mullighan CG: Acute lymphoblastic leukemia in children. N Engl J Med 373:1541-1552, 2015 - PubMed
-
- Harvey RC, Mullighan CG, Wang X, et al. : Identification of novel cluster groups in pediatric high-risk B-precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia with gene expression profiling: Correlation with genome-wide DNA copy number alterations, clinical characteristics, and outcome. Blood 116:4874-4884, 2010 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rheingold SR, Ji L, Xu X, et al. : Prognostic factors for survival after relapsed acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL): A Children’s Oncology group (COG) study. J Clin Oncol 37, 2019. (15_suppl; abstr 10008)
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- U24 CA196173/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA293366/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA015704/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 CA197695/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 CA148529/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- RC4 CA156329/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA021765/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180899/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180886/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA098413/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN261201500003C/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA114766/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN261201500003I/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA098543/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

