Synchronicity of the Gulf Stream path downstream of Cape Hatteras and the region of maximum wind stress curl
- PMID: 39122733
- PMCID: PMC11315899
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-68461-0
Synchronicity of the Gulf Stream path downstream of Cape Hatteras and the region of maximum wind stress curl
Abstract
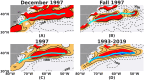
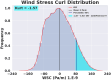
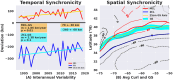
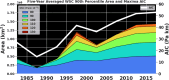
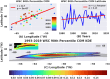
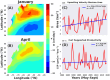
The Gulf Stream, a major ocean current in the North Atlantic ocean is a key component in the global redistribution of heat and is important for marine ecosystems. Based on 27 years (1993-2019) of wind reanalysis and satellite altimetry measurements, we present observational evidence that the path of this freely meandering jet after its separation from the continental slope at Cape Hatteras, aligns with the region of maximum cyclonic vorticity of the wind stress field known as the positive vorticity pool. This synchronicity between the wind stress curl maximum region and the Gulf Stream path is observed at multiple time-scales ranging from months to decades, spanning a distance of 1500 km between 70 and 55W. The wind stress curl in the positive vorticity pool is estimated to drive persistent upward vertical velocities ranging from 5 to 17 cm day-1 over its ~ 400,000 km2 area; this upwelling may supply a steady source of deep nutrients to the Slope Sea region, and can explain as much as a quarter of estimated primary productivity there.
© 2024. This is a U.S. Government work and not under copyright protection in the US; foreign copyright protection may apply.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Joyce, T. M., Kwon, Y. O. & Yu, L. On the relationship between synoptic wintertime atmospheric variability and path shifts in the Gulf Stream and the Kuroshio Extension. J. Clim.22, 3177–3192 (2009).10.1175/2008JCLI2690.1 - DOI
-
- Zhang, R. et al. A review of the role of the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation in Atlantic multidecadal variability and associated climate impacts. Rev. Geophys.57(2), 316–375 (2019).10.1029/2019RG000644 - DOI
-
- Andres, M. On the recent destabilization of the Gulf Stream path downstream of Cape Hatteras. Geophys. Res. Lett.43, 9836–9842 (2016).10.1002/2016GL069966 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

