Comprehensive molecular characterization of collecting duct carcinoma for therapeutic vulnerability
- PMID: 39122888
- PMCID: PMC11393068
- DOI: 10.1038/s44321-024-00102-5
Comprehensive molecular characterization of collecting duct carcinoma for therapeutic vulnerability
Abstract
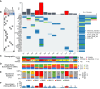
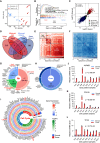
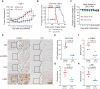
Collecting duct carcinoma (CDC) is an aggressive rare subtype of kidney cancer with unmet clinical needs. Little is known about its underlying molecular alterations and etiology, primarily due to its rarity, and lack of preclinical models. This study aims to comprehensively characterize molecular alterations in CDC and identify its therapeutic vulnerabilities. Through whole-exome and transcriptome sequencing, we identified KRAS hotspot mutations (G12A/D/V) in 3/13 (23%) of the patients, in addition to known TP53, NF2 mutations. 3/13 (23%) patients carried a mutational signature (SBS22) caused by aristolochic acid (AA) exposures, known to be more prevalent in Asia, highlighting a geologically specific disease etiology. We further discovered that cell cycle-related pathways were the most predominantly dysregulated pathways. Our drug screening with our newly established CDC preclinical models identified a CDK9 inhibitor LDC000067 that specifically inhibited CDC tumor growth and prolonged survival. Our study not only improved our understanding of oncogenic molecular alterations of Asian CDC, but also identified cell-cycle machinery as a therapeutic vulnerability, laying the foundation for clinical trials to treat patients with such aggressive cancer.
Keywords: Cell-Cycle Machinery; Collecting Duct Carcinoma; Drug Screening; Transcriptome Profiling; Whole Exome Sequencing.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures


References
-
- Bratslavsky G, Gleicher S, Jacob JM, Sanford TH, Shapiro O, Bourboulia D, Gay LM, Andrea Elvin J, Vergilio JA, Suh J et al (2021) Comprehensive genomic profiling of metastatic collecting duct carcinoma, renal medullary carcinoma, and clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Urol Oncol 39:367 e361–367.e365 10.1016/j.urolonc.2020.12.009 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2022YFA1304000/MOST | National Key Research and Development Program of China (NKPs)
- 82320108015/MOST | National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC)
- 82073391/MOST | National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC)
- 82170188/MOST | National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC)
- 2022B01J1004/Bureau of Science and Information Technology of Guangzhou Municipality | Guangzhou Municipal Science and Technology Program key projects (Guangzhou Science and Technology Program key projects)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

