High Interleukin 21 Levels in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Association with Clinical Variables and rs2221903 Polymorphism
- PMID: 39124778
- PMCID: PMC11313274
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13154512
High Interleukin 21 Levels in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Association with Clinical Variables and rs2221903 Polymorphism
Abstract
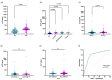
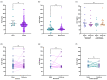
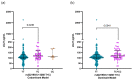
Background: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disease characterized by autoantibody production and diverse tissue and organ inflammatory affections. Interleukin 21 (IL-21) is implicated in B cell survival, proliferation, differentiation, class switching, and immunoglobulin production; therefore, it is considered a key cytokine in the pathogenesis of SLE. However, its association with disease activity and clinical phenotypes remains unclear. We aimed to evaluate the association of IL-21 levels with the disease activity and clinical phenotypes in patients with SLE. Also, we analyzed the IL21 polymorphisms associated with increased IL-21 levels. Methods: The IL-21 serum levels were determined using the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) method. The rs2221903 and rs2055979 polymorphisms were assessed in 300 healthy controls (HCs) and 300 patients with SLE by the polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP) technique. The levels of IL-21 were monitored during follow-up visits in 59 patients with SLE. Results: The patients with SLE showed higher IL-21 levels compared to the HCs. The IL-21 levels did not correlate with Mex-SLEDAI and were not different in patients with inactive, mild-moderate, and severe disease. The IL-21 levels were increased in patients with hematological affection. The ROC curve analysis revealed that the IL-21 levels had good predictive power in discriminating among patients with SLE and HCs. In a follow-up analysis, the levels of IL-21 remained higher in the patients with SLE even when the patients were in remission. Also, the rs2221903 polymorphism was associated with increased IL-21 levels. Conclusions: This study highlights the importance of IL-21 as a key cytokine in SLE. IL-21 levels are higher in patients with SLE and remain increased regardless of disease activity. According to the ROC analysis, IL-21 is a potential biomarker of SLE. Further longitudinal studies are needed to explore the relationship between IL-21 and the clinical phenotypes of SLE.
Keywords: IL21 polymorphism; Interleukin 21; systemic lupus erythematosus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bengtsson A.A., Sturfelt G., Truedsson L., Blomberg J., Alm G., Vallin H., Rönnblom L. Activation of Type I Interferon System in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Correlates with Disease Activity but Not with Antiretroviral Antibodies. Lupus. 2016;9:664–671. doi: 10.1191/096120300674499064. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Duarte A.L.B.P., Dantas A.T., De Ataíde Mariz H., Dos Santos F.A., Da Silva J.C., Da Rocha L.F., Galdino S.L., Galdino Da Rocha Pitta M. Decreased Serum Interleukin 27 in Brazilian Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2013;40:4889–4892. doi: 10.1007/s11033-013-2588-1. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Robak E., Kulczycka-Siennicka L., Gerlicz Z., Kierstan M., Korycka-Wolowiec A., Sysa-Jedrzejowska A. Correlations between Concentrations of Interleukin (IL)-17A, IL-17B and IL-17F, and Endothelial Cells and Proangiogenic Cytokines in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2013;24:60–68. doi: 10.1684/ecn.2013.0330. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

