Investigation of the Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Bioactive Compounds from Olea europaea: In Silico Evaluation of Cyclooxygenase Enzyme Inhibition and Pharmacokinetic Profiling
- PMID: 39124908
- PMCID: PMC11314539
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29153502
Investigation of the Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Bioactive Compounds from Olea europaea: In Silico Evaluation of Cyclooxygenase Enzyme Inhibition and Pharmacokinetic Profiling
Abstract
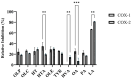
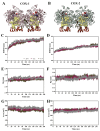
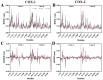
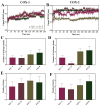
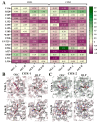
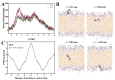
In a landmark study, oleocanthal (OLC), a major phenolic in extra virgin olive oil (EVOO), was found to possess anti-inflammatory activity similar to ibuprofen, involving inhibition of cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes. EVOO is a rich source of bioactive compounds including fatty acids and phenolics; however, the biological activities of only a small subset of compounds associated with Olea europaea have been explored. Here, the OliveNetTM library (consisting of over 600 compounds) was utilized to investigate olive-derived compounds as potential modulators of the arachidonic acid pathway. Our first aim was to perform enzymatic assays to evaluate the inhibitory activity of a selection of phenolic compounds and fatty acids against COX isoforms (COX-1 and COX-2) and 15-lipoxygenase (15-LOX). Olive compounds were found to inhibit COX isoforms, with minimal activity against 15-LOX. Subsequent molecular docking indicated that the olive compounds possess strong binding affinities for the active site of COX isoforms, and molecular dynamics (MD) simulations confirmed the stability of binding. Moreover, olive compounds were predicted to have favorable pharmacokinetic properties, including a readiness to cross biological membranes as highlighted by steered MD simulations and umbrella sampling. Importantly, olive compounds including OLC were identified as non-inhibitors of the human ether-à-go-go-related gene (hERG) channel based on patch clamp assays. Overall, this study extends our understanding of the bioactivity of Olea-europaea-derived compounds, many of which are now known to be, at least in part, accountable for the beneficial health effects of the Mediterranean diet.
Keywords: Olea europaea; anti-inflammatory; cyclooxygenase enzymes; oleocanthal; oleohydroxypyretol; olive phenolics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification and Evaluation of Olive Phenolics in the Context of Amine Oxidase Enzyme Inhibition and Depression: In Silico Modelling and In Vitro Validation.Molecules. 2024 May 23;29(11):2446. doi: 10.3390/molecules29112446. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38893322 Free PMC article.
-
In silico characterisation of olive phenolic compounds as potential cyclooxygenase modulators. Part 1.J Mol Graph Model. 2020 Dec;101:107719. doi: 10.1016/j.jmgm.2020.107719. Epub 2020 Aug 26. J Mol Graph Model. 2020. PMID: 32898836
-
Health Effects of Phenolic Compounds Found in Extra-Virgin Olive Oil, By-Products, and Leaf of Olea europaea L.Nutrients. 2019 Aug 1;11(8):1776. doi: 10.3390/nu11081776. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31374907 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Green synthesis and two-step chromatographic separation of thiocanthal and thiocanthol: Two novel biologically active sulfur derivatives of oleocanthal and oleacein from extra virgin olive oil.Food Chem. 2025 Jan 15;463(Pt 2):141296. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2024.141296. Epub 2024 Sep 16. Food Chem. 2025. PMID: 39305667
-
The Health Benefiting Mechanisms of Virgin Olive Oil Phenolic Compounds.Molecules. 2016 Dec 16;21(12):1734. doi: 10.3390/molecules21121734. Molecules. 2016. PMID: 27999296 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Computer-Aided Drug Design in Research on Chinese Materia Medica: Methods, Applications, Advantages, and Challenges.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Mar 1;17(3):315. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17030315. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40142979 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the Anti-inflammatory Potential of Novel Chrysin Derivatives through Cyclooxygenase-2 Inhibition.ACS Omega. 2024 Dec 10;9(51):50491-50503. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c07938. eCollection 2024 Dec 24. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 39741845 Free PMC article.
References
-
- González-Rodríguez M., Ait Edjoudi D., Cordero-Barreal A., Farrag M., Varela-García M., Torrijos-Pulpón C., Ruiz-Fernández C., Capuozzo M., Ottaiano A., Lago F., et al. Oleocanthal, an Antioxidant Phenolic Compound in Extra Virgin Olive Oil (EVOO): A Comprehensive Systematic Review of Its Potential in Inflammation and Cancer. Antioxidants. 2023;12:2112. doi: 10.3390/antiox12122112. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

