Axial Disease in Psoriatic Arthritis: A Challenging Domain in Clinical Practice
- PMID: 39125513
- PMCID: PMC11311426
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics14151637
Axial Disease in Psoriatic Arthritis: A Challenging Domain in Clinical Practice
Abstract
Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is a chronic inflammatory condition affecting about one-third of individuals with psoriasis. Defining axial involvement in PsA (axPsA) remains debated. While rheumatologists guide clinical practice, consensus on axPsA is still lacking. This paper explores historical and upcoming definitions from the Axial Involvement in Psoriatic Arthritis (AXIS) study, which aims to establish a validated axPsA definition. Epidemiological data reveal diverse axPsA prevalence rates, emphasizing its complex relationship with peripheral arthritis and enthesitis. Unique genetic, clinical, and radiological features differentiate axPsA from ankylosing spondylitis (AS), necessitating refined classification criteria. The recommendations from the Assessment of Spondylarthritis international Society (ASAS) provide valuable guidance due to the limited direct evidence. Emerging therapies, including interleukin-23 (IL-23) inhibitors or Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, are under investigation for axPsA. Currently, secukinumab, an interleukin-17 (IL-17) inhibitor, is an evidence-based option for axPsA management. However, given the variability in individual patient responses and disease manifestations, personalized, evidence-based treatment approaches remain essential for optimizing patient outcomes. In the final section, two real-life cases illustrate the challenges in managing axPsA, emphasizing the importance of tailored therapies. Achieving precision in defining axPsA remains a formidable task, making detailed criteria essential for effective strategies and improving patient outcomes.
Keywords: biological therapy; psoriatic arthritis; spondyloarthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following conflicts of interest: L.A. has received travel support from Janssen. A.B.A.-P. reports honoraria for lectures, educational events, and support for attending meetings from Janssen, Novartis, Lilly, Pfizer, UCB and AbbVie. B.F.-S. reports honoraria for lectures, educational events, and support for attending meetings from Janssen, Novartis, Lilly, Galapagos, UCB, Pfizer, AstraZeneca and AbbVie. J.C.S.-M. reports honoraria for lectures, educational events, and support for attending meetings from Novartis, UCB, Lilly, MSD, Janssen, Pfizer, and AbbVie. A.P. reports honoraria for lectures, educational events, and support for attending meetings from Janssen, Novartis, Lilly, Amgen, MSD, UCB, Pfizer and AbbVie. S.F. reports honoraria for lectures, educational events, and support for attending meetings from Janssen, Novartis, Lilly, Galapagos, UCB and AbbVie. J.A.G.-P. reports honoraria for lectures, educational events, and support for attending meetings from AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Boehringer-Ingelheim, GSK, Galapagos, Janssen, Lilly and Otsuka, outside the submitted work. R.S. declares consulting/grant support from AbbVie, MSD, Bristol Myers Squibb, Gebro Pharma, Gilead/Galapagos, Lilly, Pfizer, Roche, Sandoz, and Sanofi. J.D.C. has received travel support from UCB and Janssen. J.R. reports honoraria for lectures, educational events, and support for attending meetings from Janssen, Novartis, Lilly, Amgen, Galapagos, MSD, UCB, Pfizer and AbbVie.
Figures
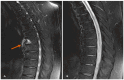
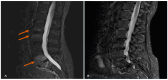
References
-
- Alinaghi F., Calov M., Kristensen L.E., Gladman D.D., Coates L.C., Jullien D., Gottlieb A.B., Gisondi P., Wu J.J., Thyssen J.P., et al. Prevalence of psoriatic arthritis in patients with psoriasis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational and clinical studies. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2019;80:251–265.e19. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2018.06.027. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mease P.J., Gladman D.D., Papp K.A., Khraishi M.M., Thaçi D., Behrens F., Northington R., Fuiman J., Bananis E., Boggs R., et al. Prevalence of rheumatologist-diagnosed psoriatic arthritis in patients with psoriasis in European/North American dermatology clinics. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2013;69:729–735. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2013.07.023. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

