Role of Intestinal Ultrasound for IBD Care: A Practical Approach
- PMID: 39125517
- PMCID: PMC11311560
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics14151639
Role of Intestinal Ultrasound for IBD Care: A Practical Approach
Abstract
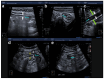
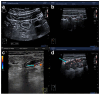
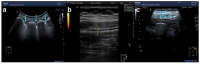
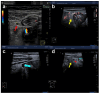
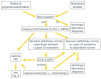
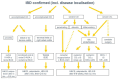
Intestinal ultrasound (IUS) has recently become the imaging technique of choice for patients with different types of intestinal inflammation. IUS has a high sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value when diagnosing Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis. Further, it is now the preferred imaging modality for routine IBD reevaluations because of its non-invasiveness, cost-effectiveness, availability (at least in Europe), and reproducibility in all age groups. However, the clinical success of IUS requires IUS training for doctors and technicians who perform IUS with a standardised description of ultrasound findings of the terminal ileum and entire colon. Complications such as abscess formation, fistulae, and stenosis can be detected by either conventional IUS or contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS). Lately, several disease activity scores have been proposed for Crohn's disease, postoperative Crohn's disease, and ulcerative colitis both in adults (including elderly) and in children. IUS was successfully used in randomised clinical trials in order to measure the treatment response. Therefore, IUS now plays a central role in clinical decision making.
Keywords: Crohn’s disease; diagnostic algorithm; imaging; standardised reporting; therapeutic algorithm; ulcerative colitis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest between the content of this paper and participation on advisory boards of several pharmaceutical companies.
Figures


References
-
- van Rheenen P.F., Aloi M., Assa A., Bronsky J., Escher J.C., Fagerberg U.L., Gasparetto M., Gerasimidis K., Griffiths A., Henderson P., et al. The Medical Management of Paediatric Crohn’s Disease: An ECCO-ESPGHAN Guideline Update. J. Crohns Colitis. 2020;15:171–194. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjaa161. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

