Diagnostic Accuracy of Non-Contrast-Enhanced Time-Resolved MR Angiography to Assess Angioarchitectural Classification Features of Brain Arteriovenous Malformations
- PMID: 39125532
- PMCID: PMC11311491
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics14151656
Diagnostic Accuracy of Non-Contrast-Enhanced Time-Resolved MR Angiography to Assess Angioarchitectural Classification Features of Brain Arteriovenous Malformations
Abstract
This study aims to assess the diagnostic accuracy of non-contrast-enhanced 4D MR angiography (NCE-4D-MRA) compared to contrast-enhanced 4D MR angiography (CE-4D-MRA) for the detection and angioarchitectural characterisation of brain arteriovenous malformations (bAVMs). Utilising a retrospective design, we examined 54 MRA pairs from 43 patients with bAVMs, using digital subtraction angiography (DSA) as the reference standard. Both NCE-4D-MRA and CE-4D-MRA were performed using a 3-T MR imaging system. The primary objectives were to evaluate the diagnostic performance of NCE-4D-MRA against CE-4D-MRA and DSA and to assess concordance between imaging modalities in grading bAVMs according to four main scales: Spetzler-Martin, Buffalo, AVM embocure score (AVMES), and R2eDAVM. Our results demonstrated that NCE-4D-MRA had a higher accuracy and specificity compared to CE-4D-MRA (0.85 vs. 0.83 and 95% vs. 85%, respectively) and similar agreement, with DSA detecting shunts in bAVMs or residuals. Concordance in grading bAVMs was substantial between NCE-4D-MRA and DSA, particularly for the Spetzler-Martin and Buffalo scales, with CE-4D-MRA showing slightly higher kappa values for interobserver agreement. The study highlights the potential of NCE-4D-MRA as a diagnostic tool for bAVMs, offering comparable accuracy to CE-4D-MRA while avoiding the risks associated with gadolinium-based contrast agents. The safety profile of imaging techniques is a significant concern in the long-term follow up of bAVMs, and further prospective research should focus on NCE-4D-MRA protocol improvement for clinical use.
Keywords: AVMES; R2DAVM; Spetzler–Martin; brain arteriovenous malformations; buffalo; contrast-enhanced MR angiography; non-contrast-enhanced MR angiography.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
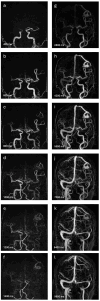
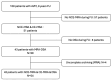
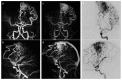
References
-
- Mohr J.P., Overbey J.R., Hartmann A., Kummer R.V., Al-Shahi Salman R., Kim H., Van Der Worp H.B., Parides M.K., Stefani M.A., Houdart E., et al. Medical management with interventional therapy versus medical management alone for unruptured brain arteriovenous malformations (ARUBA): Final follow-up of a multicentre, non-blinded, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Neurol. 2020;19:573–581. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(20)30181-2. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yu S., Yan L., Yao Y., Wang S., Yang M., Wang B., Zhuo Y., Ai L., Miao X., Zhao J., et al. Noncontrast dynamic MRA in intracranial arteriovenous malformation (AVM): Comparison with time of flight (TOF) and digital subtraction angiography (DSA) Magn. Reson. Imaging. 2012;30:869–877. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2012.02.027. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Iryo Y., Hirai T., Nakamura M., Kawano T., Kaku Y., Ohmori Y., Kai Y., Azuma M., Nishimura S., Shigematsu Y., et al. Evaluation of Intracranial Arteriovenous Malformations with Four-Dimensional Arterial-Spin Labeling–Based 3-T Magnetic Resonance Angiography. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2016;40:290–296. doi: 10.1097/RCT.0000000000000346. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fujima N., Osanai T., Shimizu Y., Yoshida A., Harada T., Nakayama N., Kudo K., Houkin K., Shirato H. Utility of noncontrast-enhanced time-resolved four-dimensional MR angiography with a vessel-selective technique for intracranial arteriovenous malformations. Magn. Reson. Imaging. 2016;44:834–845. doi: 10.1002/jmri.25222. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

