Exploring Publicly Accessible Optical Coherence Tomography Datasets: A Comprehensive Overview
- PMID: 39125544
- PMCID: PMC11312046
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics14151668
Exploring Publicly Accessible Optical Coherence Tomography Datasets: A Comprehensive Overview
Abstract
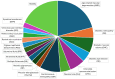
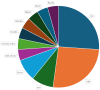
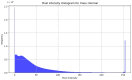
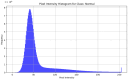
Artificial intelligence has transformed medical diagnostic capabilities, particularly through medical image analysis. AI algorithms perform well in detecting abnormalities with a strong performance, enabling computer-aided diagnosis by analyzing the extensive amounts of patient data. The data serve as a foundation upon which algorithms learn and make predictions. Thus, the importance of data cannot be underestimated, and clinically corresponding datasets are required. Many researchers face a lack of medical data due to limited access, privacy concerns, or the absence of available annotations. One of the most widely used diagnostic tools in ophthalmology is Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT). Addressing the data availability issue is crucial for enhancing AI applications in the field of OCT diagnostics. This review aims to provide a comprehensive analysis of all publicly accessible retinal OCT datasets. Our main objective is to compile a list of OCT datasets and their properties, which can serve as an accessible reference, facilitating data curation for medical image analysis tasks. For this review, we searched through the Zenodo repository, Mendeley Data repository, MEDLINE database, and Google Dataset search engine. We systematically evaluated all the identified datasets and found 23 open-access datasets containing OCT images, which significantly vary in terms of size, scope, and ground-truth labels. Our findings indicate the need for improvement in data-sharing practices and standardized documentation. Enhancing the availability and quality of OCT datasets will support the development of AI algorithms and ultimately improve diagnostic capabilities in ophthalmology. By providing a comprehensive list of accessible OCT datasets, this review aims to facilitate better utilization and development of AI in medical image analysis.
Keywords: OCT; data; data analysis; data sharing; datasets; open data; optical coherence tomography.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Ophthalmology Optical Coherence Tomography Databases for Artificial Intelligence Algorithm: A Review.Semin Ophthalmol. 2024 Apr;39(3):193-200. doi: 10.1080/08820538.2024.2308248. Epub 2024 Feb 9. Semin Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 38334303 Review.
-
An Overview of Public Retinal Optical Coherence Tomography Datasets: Access, Annotations, and Beyond.Stud Health Technol Inform. 2024 Aug 22;316:1664-1668. doi: 10.3233/SHTI240743. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2024. PMID: 39176530
-
Publicly Available Dental Image Datasets for Artificial Intelligence.J Dent Res. 2024 Dec;103(13):1365-1374. doi: 10.1177/00220345241272052. Epub 2024 Oct 18. J Dent Res. 2024. PMID: 39422586 Free PMC article.
-
Advancing glaucoma detection with convolutional neural networks: a paradigm shift in ophthalmology.Rom J Ophthalmol. 2023 Jul-Sep;67(3):222-237. doi: 10.22336/rjo.2023.39. Rom J Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 37876506 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Retinal Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT).Semin Ophthalmol. 2021 May 19;36(4):341-345. doi: 10.1080/08820538.2021.1901123. Epub 2021 Mar 18. Semin Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 33734928 Review.
Cited by
-
Deep Learning and The Retina: A New Frontier in Multiple Sclerosis Diagnosis.Curr Health Sci J. 2025 Jan-Mar;51(1):26-36. doi: 10.12865/CHSJ.51.01.03. Epub 2025 Mar 31. Curr Health Sci J. 2025. PMID: 40678297 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The march to harmonized imaging standards for retinal imaging.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2025 Jul;107:101363. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2025.101363. Epub 2025 May 11. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2025. PMID: 40360070 Review.
-
Evaluation of Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) in Identifying Retinal Conditions Through Classification of Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) Images.Cureus. 2025 Jan 7;17(1):e77109. doi: 10.7759/cureus.77109. eCollection 2025 Jan. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 39925554 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dhar T., Dey N., Borra S., Sherratt R.S. Challenges of deep learning in medical image analysis—Improving explainability and trust. IEEE Trans. Technol. Soc. 2023;4:68–75. doi: 10.1109/TTS.2023.3234203. - DOI
-
- Ker J., Wang L., Rao J., Lim T. Deep learning applications in medical image analysis. IEEE Access. 2017;6:9375–9389. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2788044. - DOI
-
- Bansal M.A., Sharma R., Kathuria M. A systematic review on data scarcity problem in deep learning: Solution and applications. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 2022;54:1–29. doi: 10.1145/3502287. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

