A Novel Affordable and Reliable Framework for Accurate Detection and Comprehensive Analysis of Somatic Mutations in Cancer
- PMID: 39125613
- PMCID: PMC11311285
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25158044
A Novel Affordable and Reliable Framework for Accurate Detection and Comprehensive Analysis of Somatic Mutations in Cancer
Abstract
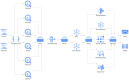
Accurate detection and analysis of somatic variants in cancer involve multiple third-party tools with complex dependencies and configurations, leading to laborious, error-prone, and time-consuming data conversions. This approach lacks accuracy, reproducibility, and portability, limiting clinical application. Musta was developed to address these issues as an end-to-end pipeline for detecting, classifying, and interpreting cancer mutations. Musta is based on a Python command-line tool designed to manage tumor-normal samples for precise somatic mutation analysis. The core is a Snakemake-based workflow that covers all key cancer genomics steps, including variant calling, mutational signature deconvolution, variant annotation, driver gene detection, pathway analysis, and tumor heterogeneity estimation. Musta is easy to install on any system via Docker, with a Makefile handling installation, configuration, and execution, allowing for full or partial pipeline runs. Musta has been validated at the CRS4-NGS Core facility and tested on large datasets from The Cancer Genome Atlas and the Beijing Institute of Genomics. Musta has proven robust and flexible for somatic variant analysis in cancer. It is user-friendly, requiring no specialized programming skills, and enables data processing with a single command line. Its reproducibility ensures consistent results across users following the same protocol.
Keywords: cancer; machine learning; mutational patterns; mutational signatures; precision medicine; somatic mutations; somatic variant detection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
AMLVaran: a software approach to implement variant analysis of targeted NGS sequencing data in an oncological care setting.BMC Med Genomics. 2020 Feb 4;13(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s12920-020-0668-3. BMC Med Genomics. 2020. PMID: 32019565 Free PMC article.
-
PipeIT: A Singularity Container for Molecular Diagnostic Somatic Variant Calling on the Ion Torrent Next-Generation Sequencing Platform.J Mol Diagn. 2019 Sep;21(5):884-894. doi: 10.1016/j.jmoldx.2019.05.001. Epub 2019 Jun 21. J Mol Diagn. 2019. PMID: 31229654
-
Evaluating somatic tumor mutation detection without matched normal samples.Hum Genomics. 2017 Sep 4;11(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s40246-017-0118-2. Hum Genomics. 2017. PMID: 28870239 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive fundamental somatic variant calling and quality management strategies for human cancer genomes.Brief Bioinform. 2021 May 20;22(3):bbaa083. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbaa083. Brief Bioinform. 2021. PMID: 32510555 Review.
-
Best practices for variant calling in clinical sequencing.Genome Med. 2020 Oct 26;12(1):91. doi: 10.1186/s13073-020-00791-w. Genome Med. 2020. PMID: 33106175 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

