PDE4D: A Multipurpose Pharmacological Target
- PMID: 39125619
- PMCID: PMC11311937
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25158052
PDE4D: A Multipurpose Pharmacological Target
Abstract
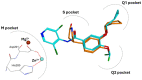
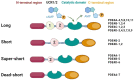
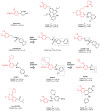
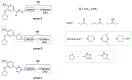
Phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) enzymes catalyze cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) hydrolysis and are involved in a variety of physiological processes, including brain function, monocyte and macrophage activation, and neutrophil infiltration. Among different PDE4 isoforms, Phosphodiesterases 4D (PDE4Ds) play a fundamental role in cognitive, learning and memory consolidation processes and cancer development. Selective PDE4D inhibitors (PDE4Dis) could represent an innovative and valid therapeutic strategy for the treatment of various neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, Huntington's, and Lou Gehrig's diseases, but also for stroke, traumatic brain and spinal cord injury, mild cognitive impairment, and all demyelinating diseases such as multiple sclerosis. In addition, small molecules able to block PDE4D isoforms have been recently studied for the treatment of specific cancer types, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma and breast cancer. This review overviews the PDE4DIsso far identified and provides useful information, from a medicinal chemistry point of view, for the development of a novel series of compounds with improved pharmacological properties.
Keywords: catechol moiety; drug design; neurodegenerative diseases; phosphodiesterases 4; phosphodiesterases 4D.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
New insights into selective PDE4D inhibitors: 3-(Cyclopentyloxy)-4-methoxybenzaldehyde O-(2-(2,6-dimethylmorpholino)-2-oxoethyl) oxime (GEBR-7b) structural development and promising activities to restore memory impairment.Eur J Med Chem. 2016 Nov 29;124:82-102. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2016.08.018. Epub 2016 Aug 13. Eur J Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 27560284
-
Amelioration of functional and histopathological consequences after spinal cord injury through phosphodiesterase 4D (PDE4D) inhibition.Neurotherapeutics. 2024 Jul;21(4):e00372. doi: 10.1016/j.neurot.2024.e00372. Epub 2024 May 16. Neurotherapeutics. 2024. PMID: 38760316 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of Second Messenger Signaling in the Brain Through PDE4 and PDE5 Inhibition: Therapeutic Implications for Neurological Disorders.Cells. 2025 Jan 9;14(2):86. doi: 10.3390/cells14020086. Cells. 2025. PMID: 39851514 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Improvement of spatial memory function in APPswe/PS1dE9 mice after chronic inhibition of phosphodiesterase type 4D.Neuropharmacology. 2014 Feb;77:120-30. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.09.015. Epub 2013 Sep 22. Neuropharmacology. 2014. PMID: 24067928
-
Phosphodiesterase-4 enzyme as a therapeutic target in neurological disorders.Pharmacol Res. 2020 Oct;160:105078. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105078. Epub 2020 Jul 14. Pharmacol Res. 2020. PMID: 32673703 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibitors of Cyclic Dinucleotide Phosphodiesterases and Cyclic Oligonucleotide Ring Nucleases as Potential Drugs for Various Diseases.Cells. 2025 Apr 30;14(9):663. doi: 10.3390/cells14090663. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40358186 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Focusing on spinal stenosis: emerging discoveries concerning Alendronate-induced risks and genetic drug targets.J Orthop Surg Res. 2025 May 4;20(1):444. doi: 10.1186/s13018-025-05854-5. J Orthop Surg Res. 2025. PMID: 40320523 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic Review: Fragile X Syndrome Across the Lifespan with a Focus on Genetics, Neurodevelopmental, Behavioral and Psychiatric Associations.Genes (Basel). 2025 Jan 25;16(2):149. doi: 10.3390/genes16020149. Genes (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40004478 Free PMC article.
-
Integration of Bioinformatics and Machine Learning Strategies Identifies Ferroptosis and Immune Infiltration Signatures in Peri-Implantitis.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 1;26(9):4306. doi: 10.3390/ijms26094306. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40362543 Free PMC article.
-
Individual contribution of PDE4B and PDE4D subfamilies to the prevention of object location memory impairments induced by sleep deprivation.Learn Mem. 2025 Jun 9;32(5-6):a054101. doi: 10.1101/lm.054101.125. Print 2025 May-Jun. Learn Mem. 2025. PMID: 40490297
References
-
- Keravis T., Lugnier C. Cyclic Nucleotide Phosphodiesterase (PDE) Isozymes as Targets of the Intracellular Signalling Network: Benefits of PDE Inhibitors in Various Diseases and Perspectives for Future Therapeutic Developments. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012;165:1288–1305. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01729.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hansen R.T., Zhang H.-T. The Past, Present, and Future of Phosphodiesterase-4 Modulation for Age-Induced Memory Loss. In: Zhang H.-T., Xu Y., O’Donnell J.M., editors. Phosphodiesterases: CNS Functions and Diseases. Volume 17. Springer International Publishing; Cham, Switzerland: 2017. pp. 169–199. Advances in Neurobiology. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

