Antioxidant Properties of Lippia alba Essential Oil: A Potential Treatment for Oxidative Stress-Related Conditions in Plants and Cancer Cells
- PMID: 39125846
- PMCID: PMC11312047
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25158276
Antioxidant Properties of Lippia alba Essential Oil: A Potential Treatment for Oxidative Stress-Related Conditions in Plants and Cancer Cells
Abstract
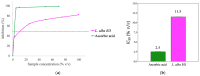
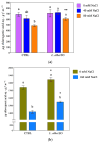
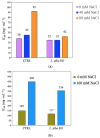
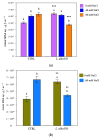
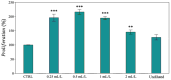
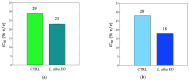
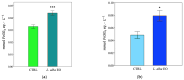
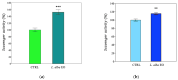
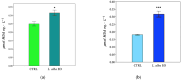
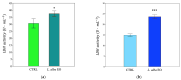
Lippia alba (Mill.) N.E.Br. ex Britton and P. Wilson is used in folk medicine of Central and South America for its biological activities: i.e., antifungal, antibacterial, antiviral, and anti-inflammatory. Based on ethnopharmacological information and the increasing interest in this species, this work aimed to test a possible wide use of its essential oil (EO) in pharmaceutical and horticultural applications. Therefore, we focused the attention on the antioxidant activity of the oil as a possible tool to overcome the oxidative stress in both applications. For this purpose, we have chosen three aggressive breast cancer cell lines and two horticultural species (Solanum lycopersicum L. and Phaseolus acutifolius L.) that are very sensitive to salt stress. We determined the antioxidant activity of L. alba EO through the quantification of phenols and flavonoids. Regarding tomato and bean plants under salt stress, L. alba EO was used for the first time as a seed priming agent to enhance plant salt tolerance. In this case, the seed treatment enhanced the content of phenolic compounds, reduced power and scavenger activity, and decreased membrane lipid peroxidation, thus mitigating the oxidative stress induced by salt. While in breast cancer cells the EO treatment showed different responses according to the cell lines, i.e., in SUM149 and MDA-MB-231 the EO decreased proliferation and increased antioxidant activity and lipid peroxidation, showing high cytotoxic effects associated with the release of lactate dehydrogenase, vice versa no effect was observed in MDA-MB-468. Such antioxidant activity opens a new perspective about this essential oil as a possible tool to counteract proliferation in some cancer cell lines and in horticulture as a seed priming agent to protect from oxidative damage in crops sensitive to salinity.
Keywords: Lippia alba; ROS; antioxidant activity; breast cancer cells; essential oil; glycophytes; phenolic compounds; salt stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Immunomodulatory, trypanocide, and antioxidant properties of essential oil fractions of Lippia alba (Verbenaceae).BMC Complement Med Ther. 2021 Jul 2;21(1):187. doi: 10.1186/s12906-021-03347-6. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2021. PMID: 34215249 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical composition and biological activities of the essential oils from Lippia alba and Lippia origanoides.An Acad Bras Cienc. 2023 Feb 10;95(1):e20220359. doi: 10.1590/0001-3765202320220359. eCollection 2023. An Acad Bras Cienc. 2023. PMID: 36790271
-
Inhibitory effect of linalool-rich essential oil from Lippia alba on the peptidase and keratinase activities of dermatophytes.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2014 Feb;29(1):12-7. doi: 10.3109/14756366.2012.743537. Epub 2013 Jan 17. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 23323991
-
Lipid stability during the frozen storage of fillets from silver catfish exposed in vivo to the essential oil of Lippia alba (Mill.) NE Brown.J Sci Food Agric. 2013 Mar 15;93(4):955-60. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.5833. Epub 2012 Aug 28. J Sci Food Agric. 2013. PMID: 22926822
-
Unraveling the Neuropharmacological Properties of Lippia alba: A Scientometric Approach.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Mar 16;18(3):420. doi: 10.3390/ph18030420. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40143196 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A comprehensive review on anti-inflammatory plants: a mechanistic insight through preclinical and clinical studies.Inflammopharmacology. 2025 May;33(5):2447-2476. doi: 10.1007/s10787-025-01764-4. Epub 2025 Jun 4. Inflammopharmacology. 2025. PMID: 40465037 Review.
References
-
- Salehi B., Azzini E., Zucca P., Maria Varoni E., Anil Kumar N.V., Dini L., Panzarini E., Rajkovic J., Valere Tsouh Fokou P., Peluso I., et al. Plant-derived bioactives and oxidative stress-related disorders: A key trend towards healthy aging and longevity promotion. Appl. Sci. 2020;10:947. doi: 10.3390/app10030947. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

