Role of Interleukin 6 in Acute Pancreatitis: A Possible Marker for Disease Prognosis
- PMID: 39125854
- PMCID: PMC11311934
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25158283
Role of Interleukin 6 in Acute Pancreatitis: A Possible Marker for Disease Prognosis
Abstract
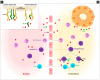
Acute pancreatitis (AP) is a significant cause of morbidity, even in children, and is frequently associated with systemic manifestations. There are many cytokines involved in the inflammatory response characteristic of this disease. Interleukin 6 (IL-6) is one of the most important cytokines involved in AP, beginning from cellular injury and continuing to the systemic inflammatory response and distant organ involvement. IL-6 is a multifunctional cytokine that regulates acute-phase response and inflammation. It is produced by various cells and exerts its biological role on many cells through its high-affinity complex receptor. IL-6 has been investigated as a predicting maker for severe forms of AP. Many studies have validated the use of IL-6 serum levels in the first 48 h as a reliable marker for severe evolution and multisystemic involvement. Still, it has not been used in daily practice until now. This review discusses the main binding mechanisms by which IL-6 triggers cellular response and the AP pathogenetic mechanisms in which IL-6 is involved. We then emphasize the promising role of IL-6 as a prognostic marker, which could be added as a routine marker at admission in children with AP.
Keywords: IL-6; acute pancreatitis; biomarker; prognosis; severity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inflammatory mediators in human acute pancreatitis: clinical and pathophysiological implications.Gut. 2000 Oct;47(4):546-52. doi: 10.1136/gut.47.4.546. Gut. 2000. PMID: 10986216 Free PMC article.
-
Does the Automatic Measurement of Interleukin 6 Allow for Prediction of Complications during the First 48 h of Acute Pancreatitis?Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jun 20;19(6):1820. doi: 10.3390/ijms19061820. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29925813 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-6 is associated with obesity, central fat distribution, and disease severity in patients with acute pancreatitis.Pancreatology. 2015 Jan-Feb;15(1):59-63. doi: 10.1016/j.pan.2014.11.001. Epub 2014 Nov 18. Pancreatology. 2015. PMID: 25434497
-
Overview of the cellular and immune mechanisms involved in acute pancreatitis: In search of new prognosis biomarkers.Expert Rev Mol Med. 2025 Jan 6;27:e9. doi: 10.1017/erm.2024.40. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 39757373 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Laboratory markers predicting severity of acute pancreatitis.Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 2015;52(6):273-83. doi: 10.3109/10408363.2015.1051659. Epub 2015 Jul 14. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 2015. PMID: 26173077 Review.
Cited by
-
Diagnostic accuracy of interleukin-6 as a biomarker for early prediction of severe acute pancreatitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Family Med Prim Care. 2025 Feb;14(2):667-674. doi: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_1366_24. Epub 2025 Feb 21. J Family Med Prim Care. 2025. PMID: 40115573 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnosis of infected pancreatic necrosis: A review of the role of blood biomarkers.Indian J Gastroenterol. 2025 Jul 2. doi: 10.1007/s12664-025-01820-5. Online ahead of print. Indian J Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40601134 Review.
-
The predictive efficacy of dynamic level changes of plasma endothelial microparticles and plasma soluble thrombomodulin on the prognosis of severe acute pancreatitis.BMC Surg. 2025 May 2;25(1):195. doi: 10.1186/s12893-025-02929-2. BMC Surg. 2025. PMID: 40316920 Free PMC article.
-
Phospholipase D2: A biomarker for stratifying disease severity in acute pancreatitis?World J Gastroenterol. 2025 Mar 21;31(11):104033. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i11.104033. World J Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40124273 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the value of blood urea nitrogen-to-albumin ratio in patients with acute pancreatitis admitted to the intensive care unit: a retrospective cohort study.Front Nutr. 2025 Apr 16;12:1435356. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1435356. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40308642 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Iannuzzi J.P., King J.A., Leong J.H., Quan J., Windsor J.W., Tanyingoh D., Coward S., Forbes N., Heitman S.J., Shaheen A.-A., et al. Global Incidence of Acute Pancreatitis Is Increasing Over Time: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Gastroenterology. 2022;162:122–134. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.09.043. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Banks P.A., Bollen T.L., Dervenis C., Gooszen H.G., Johnson C.D., Sarr M.G., Tsiotos G.G., Vege S.S., Acute Pancreatitis Classification Working Group Classification of acute pancreatitis—2012: Revision of the Atlanta classification and definitions by international consensus. Gut. 2013;62:102–111. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2012-302779. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

