Senescence in Adipose-Derived Stem Cells: Biological Mechanisms and Therapeutic Challenges
- PMID: 39125960
- PMCID: PMC11312747
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25158390
Senescence in Adipose-Derived Stem Cells: Biological Mechanisms and Therapeutic Challenges
Abstract
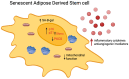
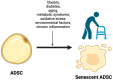
Adipose tissue-derived stem cells (ADSCs) represent a subset of the mesenchymal stem cells in every adipose compartment throughout the body. ADSCs can differentiate into various cell types, including chondrocytes, osteocytes, myocytes, and adipocytes. Moreover, they exhibit a notable potential to differentiate in vitro into cells from other germinal lineages, including endothelial cells and neurons. ADSCs have a wide range of clinical applications, from breast surgery to chronic wounds. Furthermore, they are a promising cell population for future tissue-engineering uses. Accumulating evidence indicates a decreased proliferation and differentiation potential of ADSCs with an increasing age, increasing body mass index, diabetes mellitus, metabolic syndrome, or exposure to radiotherapy. Therefore, the recent literature thoroughly investigates this cell population's senescence mechanisms and how they can hinder its possible therapeutic applications. This review will discuss the biological mechanisms and the physio-pathological causes behind ADSC senescence and how they can impact cellular functionality. Moreover, we will examine the possible strategies to invert these processes, re-establishing the full regenerative potential of this progenitor population.
Keywords: adipose-derived stem cells; ageing; diabetes; mesenchymal stem cells; senescence; senolytic drugs; stem cell therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Storti G., Scioli M.G., Kim B.-S., Terriaca S., Fiorelli E., Orlandi A., Cervelli V. Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Adipose Tissue and Extracellular Vesicles in Ovarian Cancer Patients: A Bridge toward Metastatic Diffusion or a New Therapeutic Opportunity? Cells Transplant. 2021;10:2117. doi: 10.3390/cells10082117. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cervelli V., Storti G. Novel Strategies to Improve Graft Survival and Retention. Springer International Publishing; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2022.
-
- Liu M., Lei H., Dong P., Fu X., Yang Z., Yang Y., Ma J., Liu X., Cao Y., Xiao R. Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells from the Elderly Exhibit Decreased Migration and Differentiation Abilities with Senescent Properties. Cell Transplant. 2017;26:1505–1519. doi: 10.1177/0963689717721221. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

