AI-Driven Deep Learning Techniques in Protein Structure Prediction
- PMID: 39125995
- PMCID: PMC11313475
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25158426
AI-Driven Deep Learning Techniques in Protein Structure Prediction
Abstract
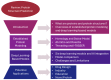
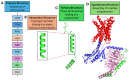
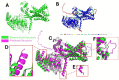
Protein structure prediction is important for understanding their function and behavior. This review study presents a comprehensive review of the computational models used in predicting protein structure. It covers the progression from established protein modeling to state-of-the-art artificial intelligence (AI) frameworks. The paper will start with a brief introduction to protein structures, protein modeling, and AI. The section on established protein modeling will discuss homology modeling, ab initio modeling, and threading. The next section is deep learning-based models. It introduces some state-of-the-art AI models, such as AlphaFold (AlphaFold, AlphaFold2, AlphaFold3), RoseTTAFold, ProteinBERT, etc. This section also discusses how AI techniques have been integrated into established frameworks like Swiss-Model, Rosetta, and I-TASSER. The model performance is compared using the rankings of CASP14 (Critical Assessment of Structure Prediction) and CASP15. CASP16 is ongoing, and its results are not included in this review. Continuous Automated Model EvaluatiOn (CAMEO) complements the biennial CASP experiment. Template modeling score (TM-score), global distance test total score (GDT_TS), and Local Distance Difference Test (lDDT) score are discussed too. This paper then acknowledges the ongoing difficulties in predicting protein structure and emphasizes the necessity of additional searches like dynamic protein behavior, conformational changes, and protein-protein interactions. In the application section, this paper introduces some applications in various fields like drug design, industry, education, and novel protein development. In summary, this paper provides a comprehensive overview of the latest advancements in established protein modeling and deep learning-based models for protein structure predictions. It emphasizes the significant advancements achieved by AI and identifies potential areas for further investigation.
Keywords: AlphaFold; artificial intelligence; bioinformatics; computational methods; deep learning; healthcare; machine learning; protein modeling; protein structure; transformer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A critical address to advancements and challenges in computational strategies for structural prediction of protein in recent past.Comput Biol Chem. 2025 Aug;117:108430. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2025.108430. Epub 2025 Mar 16. Comput Biol Chem. 2025. PMID: 40121710 Review.
-
Artificial intelligence in fusion protein three-dimensional structure prediction: Review and perspective.Clin Transl Med. 2024 Aug;14(8):e1789. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.1789. Clin Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39090739 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Progress of Protein Tertiary Structure Prediction.Molecules. 2024 Feb 13;29(4):832. doi: 10.3390/molecules29040832. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38398585 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Applying and improving AlphaFold at CASP14.Proteins. 2021 Dec;89(12):1711-1721. doi: 10.1002/prot.26257. Proteins. 2021. PMID: 34599769 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of protein structure and AI.J Hum Genet. 2024 Oct;69(10):477-480. doi: 10.1038/s10038-023-01215-4. Epub 2024 Jan 4. J Hum Genet. 2024. PMID: 38177398 Review.
Cited by
-
Isolation, characterization, and genomic analysis of a novel bacteriophage vB_Kp_XP4 targeting hypervirulent and multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae.Front Microbiol. 2025 Mar 7;16:1491961. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1491961. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40124894 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Potential of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Augmented Reality (AR) in Neurological Disease Management: A Narrative Review.Cureus. 2025 Jun 23;17(6):e86614. doi: 10.7759/cureus.86614. eCollection 2025 Jun. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40704275 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adaptive protein coevolution preserves telomere integrity.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Nov 11:2024.11.11.623029. doi: 10.1101/2024.11.11.623029. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39605578 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
ATP-Binding Cassette and Solute Carrier Transporters: Understanding Their Mechanisms and Drug Modulation Through Structural and Modeling Approaches.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Nov 27;17(12):1602. doi: 10.3390/ph17121602. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39770445 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deep learning based deconvolution methods: A systematic review.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2025 Jun 11;27:2544-2565. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2025.05.038. eCollection 2025. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2025. PMID: 40586100 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Schulz G.E., Schirmer R.H. Principles of Protein Structure. Springer Science & Business Media; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2013.
-
- Petsko G.A., Ringe D. Protein Structure and Function. New Science Press; London, UK: 2004.
-
- Law J. The development of specialties in science: The case of X-ray protein crystallography. Sci. Stud. 1973;3:275–303. doi: 10.1177/030631277300300303. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

