Advancements in the Research of New Modulators of Nitric Oxide Synthases Activity
- PMID: 39126054
- PMCID: PMC11313090
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25158486
Advancements in the Research of New Modulators of Nitric Oxide Synthases Activity
Abstract
Nitric oxide (NO) has been defined as the "miracle molecule" due to its essential pleiotropic role in living systems. Besides its implications in physiologic functions, it is also involved in the development of several disease states, and understanding this ambivalence is crucial for medicinal chemists to develop therapeutic strategies that regulate NO production without compromising its beneficial functions in cell physiology. Although nitric oxide synthase (NOS), i.e., the enzyme deputed to the NO biosynthesis, is a well-recognized druggable target to regulate NO bioavailability, some issues have emerged during the past decades, limiting the progress of NOS modulators in clinical trials. In the present review, we discuss the most promising advancements in the research of small molecules that are able to regulate NOS activity with improved pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic profiles, providing an updated framework of this research field that could be useful for the design and development of new NOS modulators.
Keywords: activators; cancer; cardiovascular diseases; drug design; inflammation; inhibitors; natural sources; neurodegenerative diseases; nitric oxide; nitric oxide synthase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



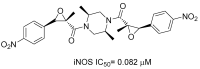

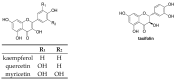
Similar articles
-
Advances in the Regulation of Inflammatory Mediators in Nitric Oxide Synthase: Implications for Disease Modulation and Therapeutic Approaches.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 30;26(3):1204. doi: 10.3390/ijms26031204. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39940974 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nitric oxide synthase inhibition and oxidative stress in cardiovascular diseases: possible therapeutic targets?Pharmacol Ther. 2013 Dec;140(3):239-57. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2013.07.004. Epub 2013 Jul 13. Pharmacol Ther. 2013. PMID: 23859953 Review.
-
Nitric oxide synthase inhibitors: a review of patents from 2011 to the present.Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2015 Jan;25(1):49-68. doi: 10.1517/13543776.2014.979154. Epub 2014 Nov 7. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2015. PMID: 25380586 Review.
-
Drugs targeting nitric oxide synthase for migraine treatment.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2014 Aug;23(8):1141-8. doi: 10.1517/13543784.2014.918953. Epub 2014 May 12. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2014. PMID: 24818644 Review.
-
Inducible nitric oxide synthase: Good or bad?Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 Sep;93:370-375. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.06.036. Epub 2017 Jun 24. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 28651238 Review.
Cited by
-
Nitric Oxide Signaling and Sensing in Age-Related Diseases.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Oct 9;13(10):1213. doi: 10.3390/antiox13101213. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39456466 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Discovery of N-[2-(4-methylquinolin-2-yl)phenyl]acetamidine as a new potent nitric oxide synthase inhibitor against glioma progression.Mol Divers. 2025 Aug 5. doi: 10.1007/s11030-025-11309-0. Online ahead of print. Mol Divers. 2025. PMID: 40764892
-
Is Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase (iNOS) Promising as a New Target Against Pulmonary Hypertension?Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 Mar 21;14(4):377. doi: 10.3390/antiox14040377. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40298665 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Brenman J.E., Chao D.S., Gee S.H., McGee A.W., Craven S.E., Santillano D.R., Wu Z., Huang F., Xia H., Peters M.F. Interaction of nitric oxide synthase with the postsynaptic density protein PSD-95 and alpha1-syntrophin mediated by PDZ domains. Cell. 1996;84:757–767. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81053-3. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

