The role of the ALKBH5 RNA demethylase in invasive breast cancer
- PMID: 39127986
- PMCID: PMC11317455
- DOI: 10.1007/s12672-024-01205-8
The role of the ALKBH5 RNA demethylase in invasive breast cancer
Abstract
Background: N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is the most common internal RNA modification and is involved in regulation of RNA and protein expression. AlkB family member 5 (ALKBH5) is a m6A demethylase. Given the important role of m6A in biological mechanisms, m6A and its regulators, have been implicated in many disease processes, including cancer. However, the contribution of ALKBH5 to invasive breast cancer (BC) remains poorly understood. The aim of this study was to evaluate the clinicopathological value of ALKBH5 in BC.
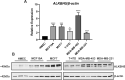
Methods: Publicly available data were used to investigate ALKBH5 mRNA alterations, prognostic significance, and association with clinical parameters at the genomic and transcriptomic level. Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) and enriched pathways with low or high ALKBH5 expression were investigated. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) was used to assess ALKBH5 protein expression in a large well-characterised BC series (n = 1327) to determine the clinical significance and association of ALKBH5 expression.
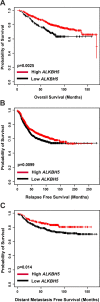
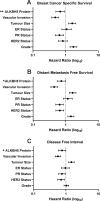
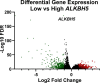
Results: Reduced ALKBH5 mRNA expression was significantly associated with poor prognosis and unfavourable clinical parameters. ALKBH5 gene harboured few mutations and/or copy number alternations, but low ALKBH5 mRNA expression was seen. Patients with low ALKBH5 mRNA expression had a number of differentially expressed genes and enriched pathways, including the cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction pathway. Low ALKBH5 protein expression was significantly associated with unfavourable clinical parameters associated with tumour progression including larger tumour size and worse Nottingham Prognostic Index group.
Conclusion: This study implicates ALKBH5 in BC and highlights the need for further functional studies to decipher the role of ALKBH5 and RNA m6A methylation in BC progression.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Epitranscriptomics; N6-methyladenosine; Prognosis; m6A.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures



Similar articles
-
RNA demethylase ALKBH5 prevents pancreatic cancer progression by posttranscriptional activation of PER1 in an m6A-YTHDF2-dependent manner.Mol Cancer. 2020 May 19;19(1):91. doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-01158-w. Mol Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32429928 Free PMC article.
-
RNA demethylase ALKBH5 promotes colorectal cancer progression by posttranscriptional activation of RAB5A in an m6A-YTHDF2-dependent manner.Clin Transl Med. 2023 May;13(5):e1279. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.1279. Clin Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 37203239 Free PMC article.
-
The N6-Methyladenosine Regulator ALKBH5 Mediated Stromal Cell-Macrophage Interaction via VEGF Signaling to Promote Recurrent Spontaneous Abortion: A Bioinformatic and In Vitro Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 13;23(24):15819. doi: 10.3390/ijms232415819. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36555463 Free PMC article.
-
Complicated role of ALKBH5 in gastrointestinal cancer: an updated review.Cancer Cell Int. 2024 Aug 24;24(1):298. doi: 10.1186/s12935-024-03480-5. Cancer Cell Int. 2024. PMID: 39182071 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The biological function of m6A demethylase ALKBH5 and its role in human disease.Cancer Cell Int. 2020 Jul 28;20:347. doi: 10.1186/s12935-020-01450-1. eCollection 2020. Cancer Cell Int. 2020. PMID: 32742194 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The role of N(6)-methyladenosine (m6a) modification in cancer: recent advances and future directions.EXCLI J. 2025 Jan 15;24:113-150. doi: 10.17179/excli2024-7935. eCollection 2025. EXCLI J. 2025. PMID: 39967906 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
