Trends in Plant-Based Diets among United States Adults, 1999-March 2020
- PMID: 39128546
- PMCID: PMC11662231
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tjnut.2024.08.004
Trends in Plant-Based Diets among United States Adults, 1999-March 2020
Abstract
Background: Interest in plant-based eating has increased alongside increased variety and availability of highly processed plant-based meat and dairy alternatives. The impact of the shifting commercial landscape and public interest in plant-based eating on dietary intake is unknown.
Objectives: To examine trends in the consumption and composition of plant-based diets in the United States adults.
Methods: Serial cross-sectional data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey were used to assess trends in the proportion of United States adults aged ≥20 y consuming a plant-based diet (defined as ≥50% total protein from plants on a 24-h dietary recall) from 1999-2000 to 2017-March 2020 (n = 51,698). Trends in processing level (percentage energy intake from ultraprocessed foods) and diet quality [Healthy Eating Index (HEI)-2020 scores] were assessed in the subset of adults consuming plant-based diets (n = 8327).
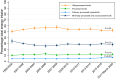
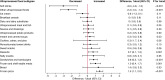
Results: The proportion of United States adults consuming plant-based diets increased from 14.4% (95% CI: 12.9%, 16.0%) to 17.2% (95% confidence interval [CI]: 15.5%, 19.1%; P = 0.005 for trend). In all survey cycles, ultraprocessed foods accounted for the majority of energy intake, and ultraprocessed food intake in plant-based diets did not significantly change over time [50.7% kcal (95% CI: 47.3%, 54.1%) in 1999-2000 compared with 52.7% kcal (95% CI: 49.7%, 55.6%) in 2017-March 2020; P for trend = 0.34]. The quality of plant-based diets, measured by HEI-2020 scores, improved from 52.1 (95% CI: 49.7, 54.6) to 55.8 (95% CI: 54.1, 57.5; P for trend <0.001).
Conclusions: Between 1999 and March 2020, the proportion of United States adults consuming a plant-based diet increased. Among people consuming plant-based diets, ultraprocessed foods contributed most to energy intake and there was no sustained change in intake over time. The mean diet quality was low but improved modestly.
Keywords: NHANES; NOVA; diet; plant-based; trend; ultraprocessed; vegetarian.
Copyright © 2024 American Society for Nutrition. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Food Insight Food and Health Survey. 2019. https://foodinsight.org/2019-food-and-health-survey/2019 [Internet]. [cited 20 December, 2023]. Available from:
-
- Gallup News Service Gallup poll social series: consumption habits [Internet] 2023. https://news.gallup.com/file/poll/510047/230824VegetarianVegan.pdf 2023 [cited 20 December, 2023]. Available from:
-
- Food Insight Food and Health Survey. 2023. https://foodinsight.org/2023-food-health-survey/2023 [Internet], 2023 [cited 20 December, 2023]. Available from:
-
- Panescu P., Carter M., Cohen M., Ignaszewski E., Murray S., O’Donnell M., et al. State of the Industry Report: plant-based meat, seafood, eggs, and dairy. https://gfi.org/resource/plant-based-meat-eggs-and-dairy-state-of-the-in... [Internet]. [cited 20 December, 2023]. Available from:
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

