Long-Term Outcomes of Heart Failure With Preserved or Mid-Range Ejection Fraction in the United States
- PMID: 39130027
- PMCID: PMC11312364
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jacadv.2024.101027
Long-Term Outcomes of Heart Failure With Preserved or Mid-Range Ejection Fraction in the United States
Abstract
Background: Approximately one-half of all heart failure (HF) consists of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) or heart failure with mid-range ejection fraction (HFmrEF). Although several recent trials have investigated treatments for HFpEF/HFmrEF, there is limited insight on the long-term clinical trajectory of this population.
Objectives: The purpose of this study was to model clinical outcomes in patients with symptomatic (NYHA functional class II-IV) HFpEF/HFmrEF over 10 years.
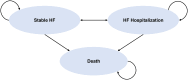
Methods: We developed a Markov model with stable HF, HF hospitalization, and death states to follow a cohort of patients with HFpEF/HFmrEF treated with standard of care (SoC) recommended by the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology/Heart Failure Society of America. Population characteristics and clinical event probabilities were derived from recent phase 3 HFpEF/HFmrEF trials. We used weighted averages for control and sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor outcomes. SoC was informed by baseline treatments reported in clinical trials.
Results: In a cohort of U.S. patients with HFpEF/HFmrEF treated with SoC, our model estimated 0.53 cumulative HF hospitalizations per patient over 10 years. Overall, 37% had at least 1 HF hospitalization, and 26% experienced cardiovascular death. The model estimated 6.1 years of life expectancy from age 72 and total cost of care over this time of $123,900.
Conclusions: HFpEF/HFmrEF is associated with high rates of HF hospitalization and cardiovascular mortality based on contemporary clinical trials in this population. Furthermore, clinical trial results are likely to be more optimistic than real-world outcomes. Continuing to optimize care and treatment may reduce clinical burden and improve population health.
Keywords: HFmrEF; HFpEF; costs; heart failure; hospitalizations; mortality.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
This work was funded by 10.13039/100015340Bayer US, LLC. Drs Sun, Dayer, Hansen, and Sullivan have received research funding for the study. Drs Du, Williamson, Kong, and Singh are employees of Bayer US, LLC.
Figures
References
-
- Tsao C.W., Aday A.W., Almarzooq Z.I., et al. Heart disease and Stroke Statistics-2022 Update: a report from the American heart association. Circulation. 2022;145(8):e153–e639. - PubMed
-
- Goyal P., Almarzooq Z.I., Horn E.M., et al. Characteristics of hospitalizations for heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Am J Med. 2016;129(6) 635.e15-26. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

