Impact of artificial sweeteners and rare sugars on the gut microbiome
- PMID: 39130663
- PMCID: PMC11315849
- DOI: 10.1007/s10068-024-01597-x
Impact of artificial sweeteners and rare sugars on the gut microbiome
Abstract
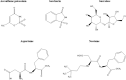
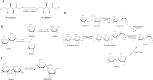
Alternative sugars are often used as sugar substitutes because of their low calories and glycemic index. Recently, consumption of these sweeteners in diet foods and beverages has increased dramatically, raising concerns about their health effects. This review examines the types and characteristics of artificial sweeteners and rare sugars and analyzes their impact on the gut microbiome. In the section on artificial sweeteners, we have described the chemical structures of different sweeteners, their digestion and absorption processes, and their effects on the gut microbiota. We have also discussed the biochemical properties and production methods of rare sugars and their positive and negative effects on gut microbial communities. Finally, we have described how artificial sweeteners and rare sugars alter the gut microbiome and how these changes affect the gut environment. Our observations aim to improve our understanding regarding the potential health implications of the consumption of artificial sweeteners and low-calorie sugars.
Keywords: Artificial sweetener; Gut microbiome; Rare sugar.
© The Korean Society of Food Science and Technology 2024. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- AlDeeb OAA, Mahgoub H, Foda NH. Chapter Ten - Sucralose. pp. 423-462. In: Profiles of Drug Substances, Excipients and Eelated Methodology. Brittain HG (ed). Academic Press (2013) - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources