[Using Artificial Intelligence Software for Diagnosing Emphysema and Interstitial Lung Disease]
- PMID: 39130780
- PMCID: PMC11310433
- DOI: 10.3348/jksr.2024.0050
[Using Artificial Intelligence Software for Diagnosing Emphysema and Interstitial Lung Disease]
Abstract
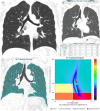
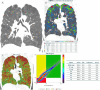
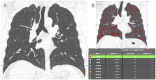
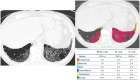
Researchers have developed various algorithms utilizing artificial intelligence (AI) to automatically and objectively diagnose patterns and extent of pulmonary emphysema or interstitial lung diseases on chest CT scans. Studies show that AI-based quantification of emphysema on chest CT scans reveals a connection between an increase in the relative percentage of emphysema and a decline in lung function. Notably, quantifying centrilobular emphysema has proven helpful in predicting clinical symptoms or mortality rates of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. In the context of interstitial lung diseases, AI can classify the usual interstitial pneumonia pattern on CT scans into categories like normal, ground-glass opacity, reticular opacity, honeycombing, emphysema, and consolidation. This classification accuracy is comparable to chest radiologists (70%-80%). However, the results generated by AI are influenced by factors such as scan parameters, reconstruction algorithms, radiation doses, and the training data used to develop the AI. These limitations currently restrict the widespread adoption of AI for quantifying pulmonary emphysema and interstitial lung diseases in daily clinical practice. This paper will showcase the authors' experience using AI for diagnosing and quantifying emphysema and interstitial lung diseases through case studies. We will primarily focus on the advantages and limitations of AI for these two diseases.
흉부 CT상 폐기종이나 간질성 폐질환의 형태나 범위를 인공지능을 이용하여 자동적으로 객관적으로 진단하는 다양한 알고리즘을 개발되고, 이를 증명하는 연구들이 진행되어 왔다. 흉부 CT상 인공지능을 이용한 폐기종 정량화 연구들을 보면 CT상 폐기종의 상대적인 양이 증가와 폐 기능의 악화와 연관이 있으며, 특히 중심성 폐기종을 중심으로 정량화를 하는 것이 임상 증상이나 만성폐쇄성 폐질환의 사망률을 예측하는 데 도움이 된다고 보고하고 있다. 또한, 간질성 폐질환에서는 인공지능이 CT상 통상성 간질성 폐렴의 형태를 정상, 간유리 음영, 망상형 음영, 벌집 모양, 폐기종, 경화로 분류를 할 수 있고, 인공지능이 흉부영상의학과 전문의와 비슷한 정도로 통상성 간질성 폐렴을 진단(70%–80%) 할 수 있다고 보고했다. 그러나 인공지능의 결과들이 흉부 CT의 스캔 변수들, 재구성 알고리즘, 방사선 선량, 개발된 인공지능 훈련 데이터에 의해 영향을 받으며, 이러한 이유로 아직까지 흉부 CT상 폐기종과 간질성 폐질환의 진단과 정량화는 실제로 일상 업무에서 제한적으로 사용되고 있다. 이 논문에서는 폐기종과 간질성 폐질환의 진단과 정량화를 위해서 인공지능을 사용하고 있는 저자들의 경험을 증례로 소개를 하고, 이 두 질환의 인공지능의 효용성과 제한점에 대해서 언급하고자 한다.
Copyrights © 2024 The Korean Society of Radiology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: Gong Yong Jin has been a Section Editor of the Journal of the Korean Society of Radiology since 2024; however, he was not involved in the peer reviewer selection, evaluation, or decision process of this article. The remaining author has declared no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Grenier PA. Deep learning assessment of emphysema progression at CT predicts outcomes. Radiology. 2022;304:680–682. - PubMed
-
- Oh AS, Lynch DA, Swigris JJ, Baraghoshi D, Dyer DS, Hale VA, et al. Deep learning-based fibrosis extent on computed tomography predicts outcome of fibrosing interstitial lung disease independent of visually assessed computed tomography pattern. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2024;21:218–227. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

